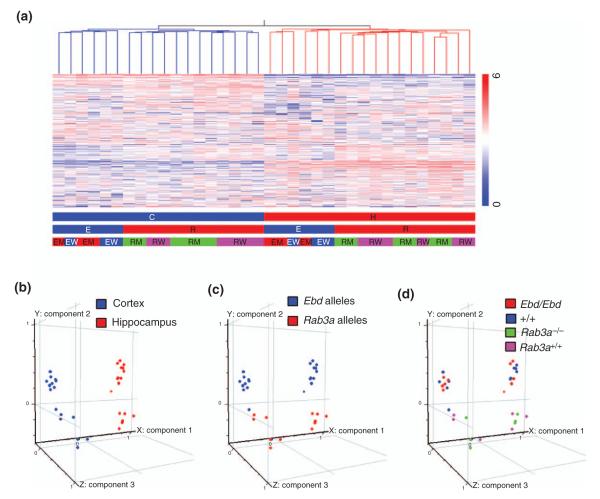
Figure 3. Global profiling of the 36 microarray samples from cortex and hippocampus of earlybird (Ebd) and Rab3a-null mutants and their wild-type littermates.
(a) Hierarchical clustering of the 20975 genes across 36 samples. Pearson correlation was used to construct the gene tree and the condition tree (only the condition tree is shown). Normalized expression values are displayed according to the vertical color bar. The horizontal bars beneath indicate the sample information: C, cortex; H, hippocampus; E, Ebd line; R, Rab3a null line; EM, Ebd/Ebd;EW, +/+ (wild-type controls of Ebd/Ebd); RM, Rab3a−/−; RW, Rab3a+/+. (b–d) Principle Component Analysis on these 36 samples. (b) Different brain regions are distributed along the first component that contributed 24.09% to the overall variance in the gene expression among these 36 samples. (c) Genetic backgrounds are distributed along the second component that had a contribution of 10.08%. (d) The four different genotypes do not show clear distribution pattern, indicating that Ebd or Rab3a-null mutation had subtle effect on gene expression.