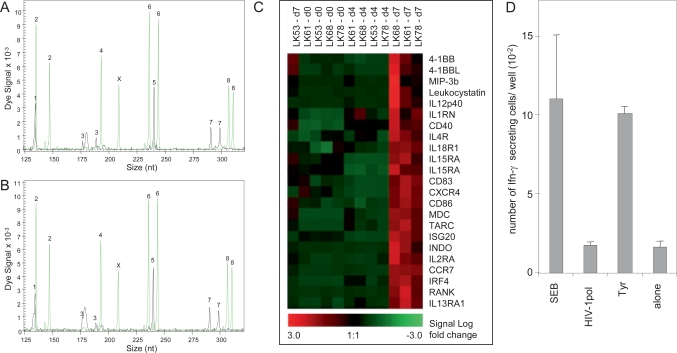
Fig. 3.
Example for characterization of dendritic cell products. STR analyses of freshly isolated CD14+ monocytes (A) and of mature dendritic cells after 7 days in cell culture (B) confirm authenticity. STR loci are numbered as in figure 1. Detection of X-amelogenin and Y-amelogenin indicates a male donor. C) Expression profiling of dendritic cells derived from CD14+ monocytes (day 0) of leukapheresis samples (LK53, LK61, LK68 and LK78) during cultivation and maturation (day 4 and day 7) using Affymetrix HG-U95a DNA arrays. Heat map of selected genes indicates changes in gene expression during maturation. Up-regulation of maturation specific genes is evident LK61, LK68 and LK78 D) Immunostimulatory function of the mature dendritic cell product was confirmed by interferon [γ] – ELISPOT assays: Tyrosinase-specific T cells were stimulated by superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin (SEB) (unspecific positive control) and specifically by tyrosinase peptide-presenting mature dendritic cells (tyr) but not by > dendritic cells alone or dendritic cells loaded with an unrelated peptide. The experiments were performed in triplicate; mean and standard deviation are shown.