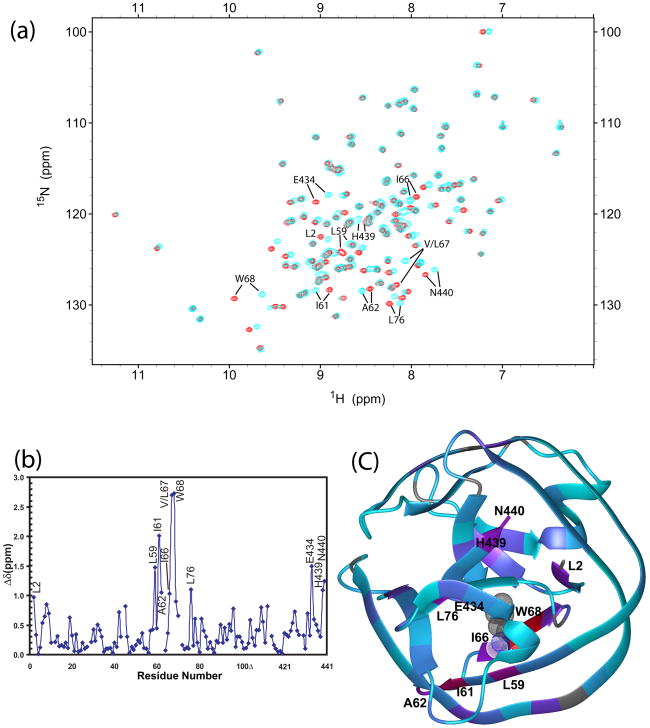
Figure 2.
The V67L mutation causes global changes, affecting the N- and C-terminus of the intein. Peaks with large chemical shift perturbations are labeled. (a) Overlay of 15N-1H HSQC spectra of ΔΔIhh-V67CM (cyan) and ΔΔIhh-L67CM (red) mutants. (b) Chemical shift difference between ΔΔIhh-V67CM and ΔΔIhh-L67CM mutants plotted against residue number. (c) Projection of V67L chemical shift perturbation onto the crystal structure ofΔΔIhh-L67CM (pdb code: 2IN8). The ribbon color is linearly interpolated between red and purple for Δδ between 3.0 and 1.0 ppm; and between purple and cyan for Δδ between 1.0 and 0 ppm. The ribbon is colored grey when chemical shift differences are not available, for prolines, N-terminal residue and unassigned residues. Residue L67 is displayed in meshed CPK mode.