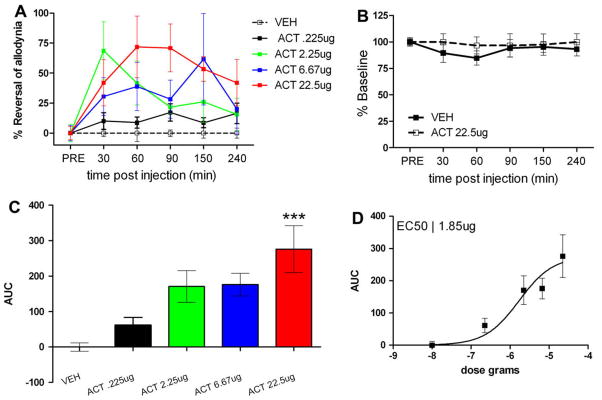
Fig. 1.
Intrathecal acetazolamide (ACT) inhibits neuropathic allodynia in the spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model. (A) Predrug mechanical withdrawal thresholds were measured and ACT was injected intrathecally and mechanical withdrawal thresholds were reassessed at the indicated time points. A significant main effect of ACT was observed (F(4, 144) = 6.95, p < 0.0001). (B) ACT, at the highest dose given, did not alter mechanical withdrawal thresholds in sham animals. (C) ACT dose-dependently inhibited neuropathic allodynia with an EC50 (D) of 1.85 ± 3.3 μg. ***p < 0.001 with one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post hoc test.