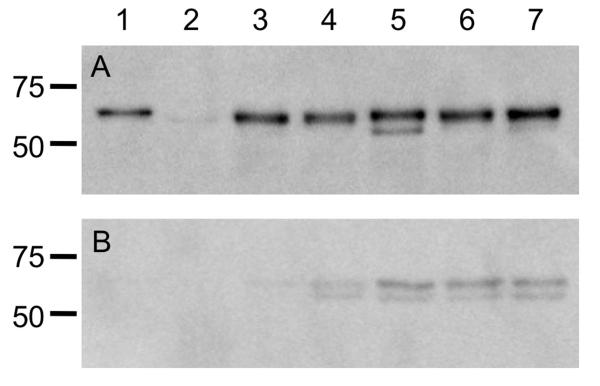
Figure 3. Immunoblots of mutants and transformed strains.
Analysis of FlaA and FlaB protein synthesis in the C. jejuni F38011 wild-type strain, F38011 flaAB mutant, and transformed mutants. Whole cell lysates were prepared from broth cultures of C. jejuni in mid-exponential growth phase, and separated in 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Panels: A) Whole cell lysates; and B) Supernatants were electrophoretically transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane and the immunoblots were probed with a polyclonal serum that recognizes both FlaA and FlaB. The samples in each lane are the: 1) C. jejuni F38011 wild-type strain; 2) C. jejuni F38011 flaAB mutant; 3) C. jejuni F38011 flaAB mutant harboring PflaA-flaA; 4) C. jejuni F38011 flaAB mutant harboring PflaA-flaB; 5) C. jejuni F38011 flaAB mutant harboring PflaA-flaAD0BD123BD0; 6) C. jejuni F38011 flaAB mutant harboring harboring PflaA-flaBD0BD123AD0; and 7) C. jejuni F38011 flaAB mutant harboring PflaA-flaAD0BD123AD0. The proteins loaded in the immunoblots (Panels A and B) are normalized according to culture density, so the levels of flagellin in the whole cell lysates and supernatants can be directly compared.