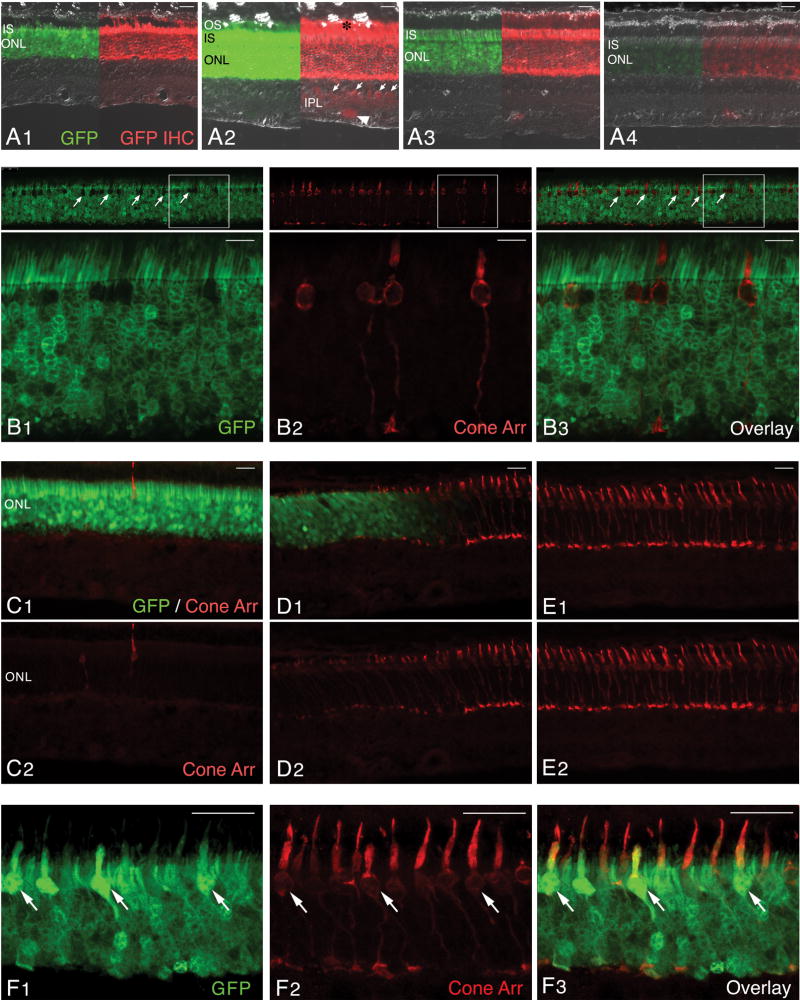
Figure 5. Transduction pattern of AAV2/5-hGRK1-GFP following subretinal delivery to the normal canine retina.
(A1–4) Native GFP fluorescence (green) and GFP immunolabeling (red) images merged with DIC/Nomarski optics; images show the GFP expression with decreasing viral vector titers. (A1) Retina of E1055-R (1.51 × 1013 vg/ml). (A2) Retina of P1476-L (1.51 × 1012 vg/ml). (A3) Retina of X235-R (1.51 × 1011 vg/ml). (A4) Retina of X235-L (1.51 × 1010 vg/ml). (B1–3) Confocal microscopy images of native GFP (green) and cone arrestin (red) immunolabeling in the injected area of retina P1476-L.(C–E) Epifluorescence microscopy images of native GFP (green) and cone arrestin (red) immunolabeling in the center (C1–2), at the border (D1–2), and outside the injected retinal area of E1055-R. (F1–3) Confocal microscopy images of native GFP (green) and cone arrestin (red) immunolabeling in the injected area of retina E1055-R.
Abbreviations: OS, outer segments; IS, inner segments; ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IHC, immunohistochemistry; Cone Arr. cone arrestin.
Scale bars: (A1–4; C1–2, D1–2, E1–2) 20 μm; (B1–3) 10 μm; (F1–3) 25 μm.