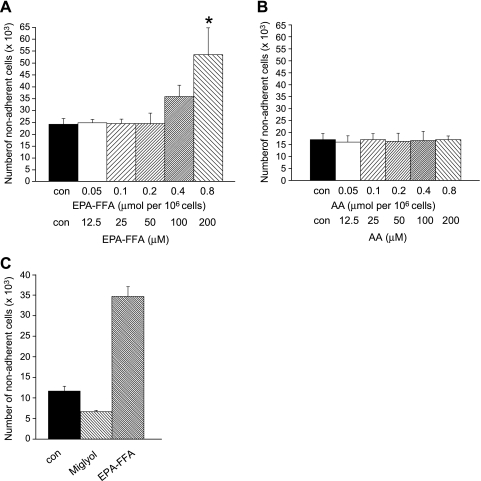
Figure 1.
EPA-FFA induces apoptosis of HCA-7 human CRC cells. (A) Apoptosis of HCA-7 human CRC cells (measured by nonadherent cell counting; [14]) after treatment with increasing amounts of EPA-FFA (quoted as micromoles per 106 cells exposure and the equivalent working micromolar concentration below that) or the equivalent dilution (0.06% vol./vol.) of 95% (vol./vol.) ethanol carrier alone (con) to 0.8 µmol of EPA-FFA/106 cells (200 µM) for 24 hours after overnight incubation of 0.5 x 106 CRC in triplicate 35-mm wells. Columns and bars represent the mean and SEM of triplicate values, respectively. Data are representative of three independent experiments. *P < .01 for the comparison with con and EPA-FFA exposure less than 0.4 µmol/106 cells (100 µM). (B) Apoptotic HCA-7 human CRC cell counts after treatment with increasing amounts of AA (quoted as micromoles per 106 cells or the micromolar concentration) or the equivalent dilution (0.06% vol./vol.) of 95% (vol./vol.) ethanol carrier alone (con) to 0.8 µmol of AA/106 cells (200 µM) for 24 hours. Columns and bars represent the mean and SEM of triplicate values, respectively. (C) Comparison of the proapoptotic activity of EPA-FFA and Miglyol 810 (both 0.8 µmol/106 cells [200 µM] in 95% [vol./vol.] ethanol) on HCA-7 human CRC cells. Con represents the equivalent dilution (0.06% vol./vol.) of 95% (vol./vol.) ethanol alone. Columns and bars represent the mean and SEM of triplicate values, respectively.