Figure 1. TTX does not block taste-evoked transmitter (ATP) release from isolated receptor (Type II) cells.
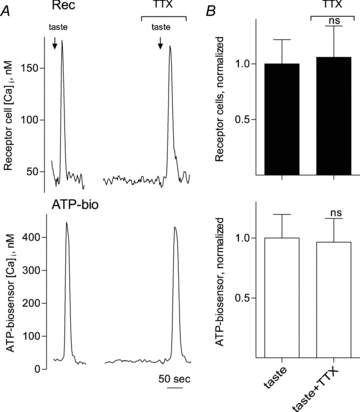
A, simultaneous recordings of Ca2+ responses from an isolated receptor cell (Rec, top) and an apposed ATP biosensor (ATP-bio, bottom) to monitor transmitter secretion during taste stimulation. The arrows above the recordings indicate application of taste mix (see Methods). Taste-evoked Ca2+ responses in the receptor cell and ATP secretion were unaffected by the presence of TTX (1 μm). B, summary of data. Bars (mean ±s.e.m.) show taste-evoked responses in receptor cells (filled bars, top) and taste-evoked ATP secretion (biosensor response, open bars, below) (N= 11 cells). Individual responses were normalized to the average of the taste-evoked responses in receptor cells (upper) or ATP-biosensor cells (lower) for all experiments in this series. No significant differences (ns) were obtained by applying 1 μm TTX. Student's paired t test.
