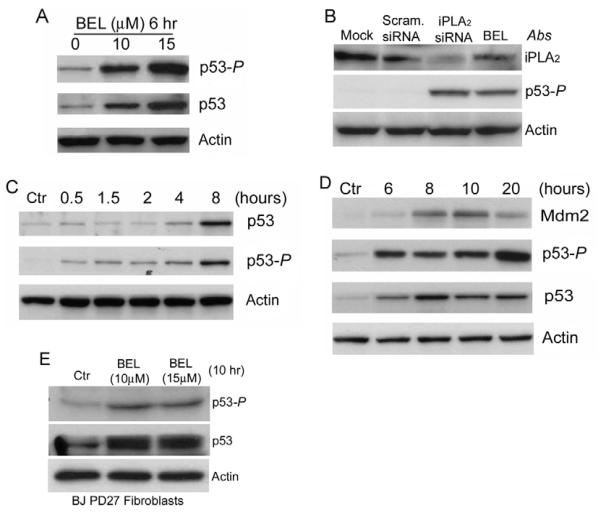
Fig. 1.
Inhibition of iPLA2 induces phosphorylation of p53 at Ser15. (A) Dose-dependent induction of p53 phosphorylation at Ser15 (p53-P) by BEL. HCT116 cells were prepared and treated with BEL for 6 hours. The cell lysates were prepared and the levels of p53-P and total p53 were determined by western blotting. Actin was used as an internal protein control. (B) siRNA silencing of iPLA2 expression induced phosphorylation of p53. HCT116 cells were transfected with mock, scramble siRNA and siRNA specifically targeting iPLA2. The samples were analyzed by western blotting for iPLA2, p53-P and actin. (C) Time course of BEL-induced p53-P in HCT116 cells. HCT116 cells were treated with 15 μM BEL for the times indicated. p53-P levels were assessed at each time point by western blotting. (D) BEL-induced p53 activation and MDM2 expression. HCT116 cells were incubated with BEL (12.5 μM) or vehicle for up to 20 hours and the levels of p53, p53-P and MDM2 were analyzed by western blotting. (E) BEL-induced p53 phosphorylation in primary human foreskin fibroblast BJ PD27 cells. BJ PD27 cells were prepared and treated with BEL for 10 hours. The cell lysates were prepared and the levels of iPLA2, p53-P and actin were determined by western blotting.