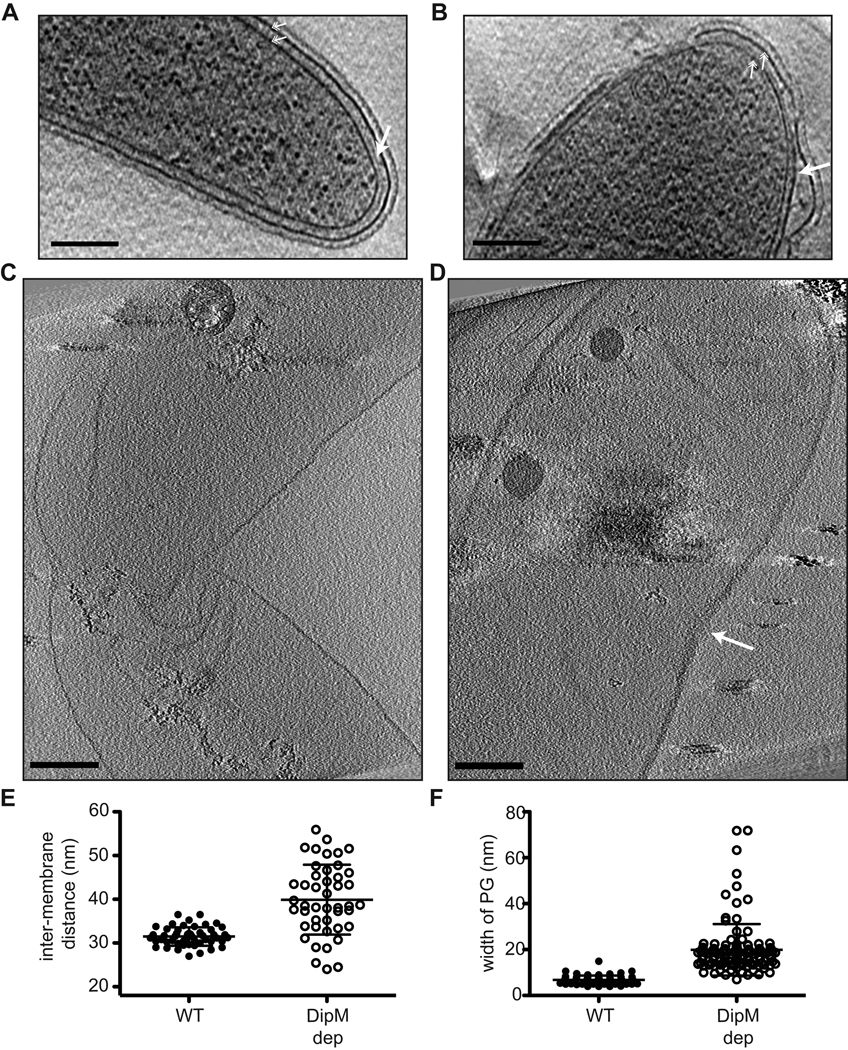
Figure 6.
DipM is required for maintenance of proper PG width. A and B. Tomographic slices of wild type (CB15N) (A) and DipM-depleted (EG353) (B) cells. Arrow indicates PG. Hatched arrows indicate inner and outer membranes. CB15N was grown in PYE, EG353 cells were grown as in 5D. Bar = 200 nm. C and D. Slices through 3D cryoET reconstructions of sacculi isolated from wild type (C) and DipM-depleted (EG353) cells. Arrow indicates division site in DipM depleted sacculus. Bar = 200 nm. E. Scatter dot plot of inter-membrane distances in wild type (WT) and DipM-depleted cells (calculated from images as in A and B). Mean and standard deviation are plotted. F. Scatter dot plot of PG width in sacculi from wild type and DipM-depleted cells (calculated from images as in C and D). Mean and standard deviation are plotted.