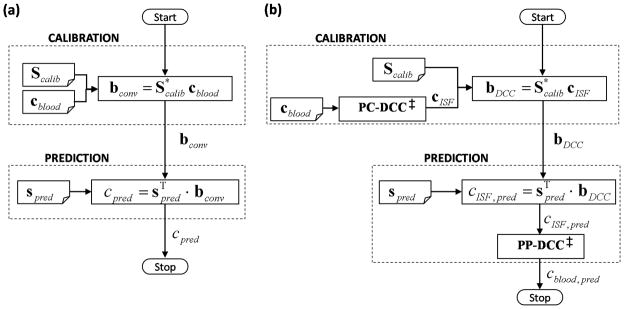
Fig. 1.
Flowcharts of (a) the conventional implicit and (b) DCC calibration methods. Scalib, cblood, and spred represent the calibration spectra, reference blood glucose concentrations in the calibration samples, and the spectrum acquired from the prediction sample, respectively. For the conventional calibration method, bconv and cpred give the regression vector and the predicted concentration, respectively. For DCC calibration, bDCC represents the developed regression vector. cISF,pred and cblood,pred are the intermediate ISF glucose estimate and the final blood glucose prediction. PC-DCC is the pre-calibration transformation of blood glucose concentrations into the corresponding ISF glucose values. PP-DCC transforms the predicted ISF glucose concentration into the blood glucose value. Note that the conventional calibration scheme does not differentiate between the blood and ISF glucose concentrations.
‡ Both PP-DCC and PC-DCC require two concentration inputs acquired at a time interval Δt apart for evaluation of Eq. (15) and (16), respectively.