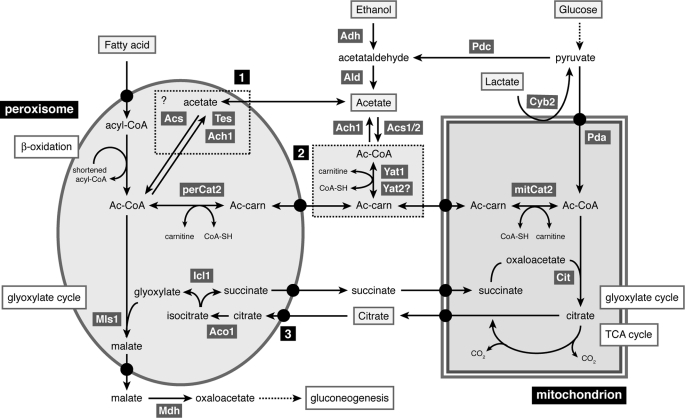
FIGURE 6.
Model showing the interorganellar flow of acetyl units in C. albicans. Depicted biochemical pathways are β-oxidation of fatty acids, glyoxylate cycle, and tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Ach1, acetyl-CoA hydrolase; Aco, aconitase; Acs1/2, acetyl-CoA synthase; Adh, alcohol dehydrogenase; Ald, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase; Cit, citrate synthase; Cyb2, l-lactate dehydrogenase; Icl1, isocitrate lyase; mitCat2, mitochondrial Cat2; Mls1, malate synthase; Pda, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; Pdc, pyruvate decarboxylase; perCat2, peroxisomal Cat2; Tes, thioesterase; Yat1/2, (putative) carnitine acetyltransferases. Box 1, alternative pathway for transport of acetyl units across the peroxisomal membrane in the form of acetate; Box 2, cytosolic carnitine acetyltransferases; 3, putative transport deficiency in the mitCAT2 strain. For details, see “Discussion.”