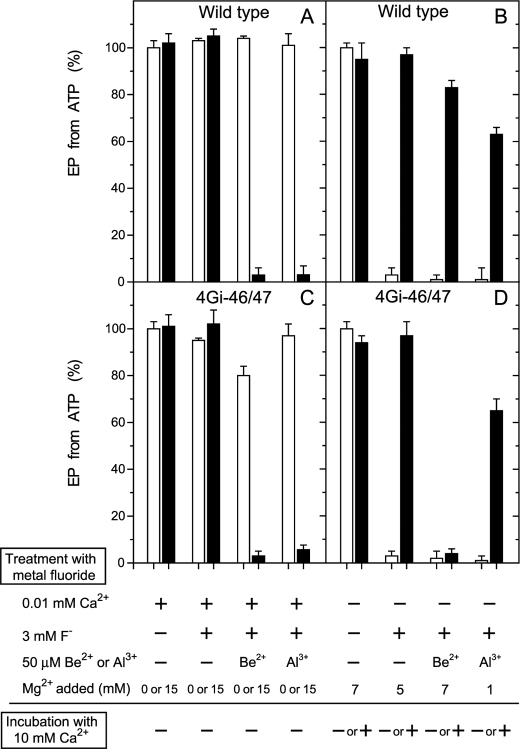
FIGURE 3.
Inhibition of EP formation from ATP by metal fluoride. A and C, microsomes expressing the wild type or mutant 4Gi-46/47 (0.35 mg/ml) were treated at 25 °C for 30 min with metal fluoride in the presence of 0.01 mm Ca2+ (0.01 mm CaCl2 without EGTA) in 3 mm KF plus 50 μm BeSO4 or AlCl3, 0.1 m KCl, and 50 mm MOPS/Tris (pH 7) with (black bar) or without (white bar) 15 mm MgCl2. Subsequently, the samples were diluted 10-fold and phosphorylated at 0 °C for 15 s with 10 μm [γ-32P]ATP in 1 μm A23187, 0.1 mm Ca2+ (0.5 mm CaCl2 with 0.4 mm EGTA), 7 mm MgCl2, 0.1 m KCl, and 50 mm MOPS/Tris (pH 7), and the amount of EP formed was determined. The amount of EP formed with the wild type in the control sample, i.e. incubated without the fluoride compounds and Mg2+ (4.7 nmol/mg of the expressed SERCA1a), was normalized to 100%. The amount of EP formed with the mutant 4Gi-46/47 in the control sample was almost the same as that of wild type. B and D, microsomes were treated with metal fluoride in the absence of Ca2+ (1 mm EGTA without added CaCl2) and in the presence of the indicated concentrations of MgCl2. Subsequently, the samples were diluted 2.5-fold with a solution containing 1 μm A23187, 0.1 m KCl, 50 mm MOPS/Tris (pH 7), and EGTA (to give 1 mm, white bar) or CaCl2 (to give 10 mm Ca2+, black bar) and incubated at 25 °C for 1 h. The samples were then further diluted 10-fold and phosphorylated with 10 μm [γ-32P]ATP and 0.1 mm Ca2+ as in A and C, and the amount of EP formed was determined.