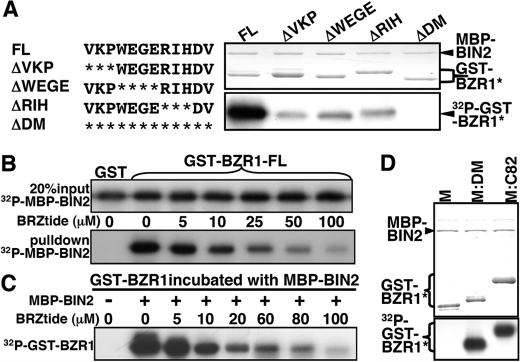
FIGURE 5.
12-Amino acid BIN2-DM is necessary and sufficient for BIN2 to bind and phosphorylate BZR1. A, in vitro phosphorylation assay of the full-length wild-type (FL) or a mutated GST-BZR1 fusion protein lacking 3 or 4 amino acids (ΔVKP, ΔWEGE, or ΔRIH) or the entire BIN2-DM (ΔDM). The amino acid sequence of the BIN2-DM is shown on the left, and asterisks indicate deleted amino acids. B, GST pulldown assay was performed to test if a BIN2-DM (underlined amino acids)-containing peptide (306NSQVKPWEGERIHDV320, named as BZRtide) inhibits the BIN2/BZR1 interaction. Equal amounts of 32P-labeled MBP-BIN2 (the upper panel) were incubated with equal amounts of the full-length GST-BZR1 fusion protein bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads and different concentrations of BZRtide, and the amounts of pulled down MBP-BIN2 were revealed by autoradiography (the lower panel). C, BZRtide competitively inhibits the BIN2-catalyzed BZR1 phosphorylation by preventing the BIN2-BZR1 interaction. Equal amounts of GST-BZR1 were incubated with equal amounts of MBP-BIN2 but different concentrations of BZRtide in a 30-μl GSK3 kinase assay solution (20), and the levels of phosphorylation were revealed by autoradiography of an SDS-polyacrylamide gel that separates the reaction mixtures. D, GST-tagged M, M:C82, or the M:DM (the M fragment fused to the BIN2-DM) fusion protein was tested for phosphorylation by MBP-BIN2. The upper panel shows the amount of proteins used in the kinase assay by Coomassie Blue staining, and the lower panel indicates the levels of phosphorylation by autoradiography.