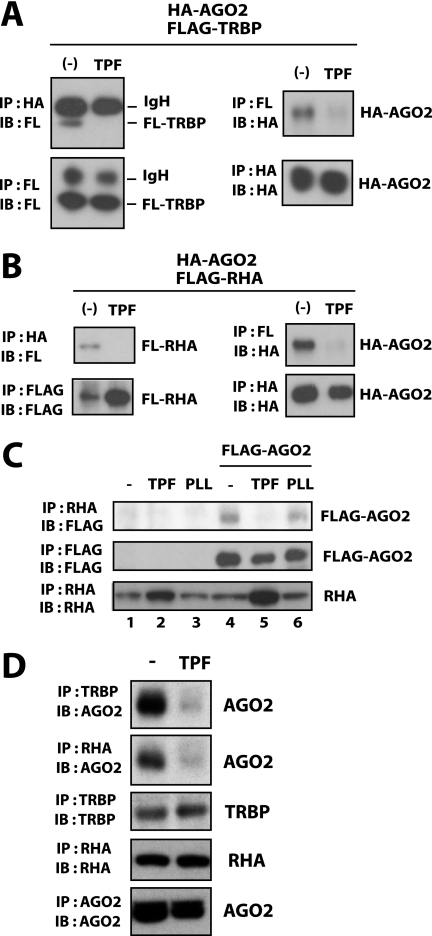
FIGURE 3.
TPF disrupts the association of TRBP and RHA with AGO2. A and B, 293T cells were transfected with HA-tagged AGO2 (HA-AGO2) and FLAG-tagged TRBP (FLAG-TRBP in A) or RHA (FLAG-RHA in B). At 24 h post transfection, cells were treated without or with TPF. After a further 24 h, cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG or anti-HA. The immunoprecipitates were blotted with anti-FLAG or anti-HA as indicated. In the left panels of A, the recovered bands for the IgG heavy chain (IgH) as well as for FLAG-TRBP are indicated. Recovery of HA-AGO2 is shown in the right panels. In B, recoveries of FLAG-RHA and HA-AGO2 are shown. C, 293T cells transfected with FLAG·AGO2 (lanes 4–6) or the corresponding empty vector (lanes 1–3) were treated with TPF (lanes 2 and 5), PLL (lanes 3 and 6), or were untreated (lanes 1 and 4). Cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-RHA (top and bottom) or anti-FLAG (middle). The immunoprecipitates were blotted with anti-FLAG (top and middle) or anti-RHA (bottom). D, after 24-h treatment with TPF or untreated (−), 293T cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-TRBP, anti-RHA, or anti-AGO2 as indicated. The immunoprecipitates were blotted with anti-AGO2, anti-TRBP, or anti-RHA. Endogenous AGO2 co-precipitated with TRBP or RHA was decreased in cells treated with TPF.