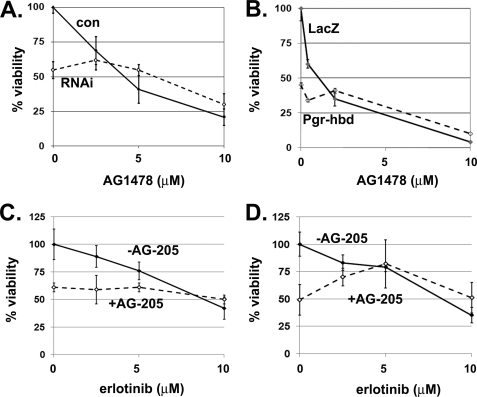
FIGURE 1.
Disrupting Pgrmc1 function suppresses sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors. A, A549/con (solid line) or A549/RNAi (dashed line) cells were maintained in media lacking serum and treated with 2.5–10 μm EGFR inhibitor AG1478 for 96 h. Percent viability was determined by cell counting, and for all of the panels % viability refers to the cell density relative to untreated cells. B, AG1478 susceptibility in Ad-LacZ and Ad-Pgr-hbd-infected A549 cells, were measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay 4 days after infection in serum-free media containing increasing doses of AG1478. Solid lines represent cells infected with the control Ad-LacZ, whereas Ad-Pgr-hbd-infected cells are indicated by a dashed line. C, A549 cells were treated with vehicle (solid line) or 10 μm AG-205 (dashed line) plus increasing doses of erlotinib and counted. D, MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells were treated with AG-205 and erlotinib as described in panel C. Each of the experiments is representative of experiments performed at least in triplicate. The results indicate that increases in proliferation in Pgrmc1-expressing cells are reversed by EGFR inhibitors.