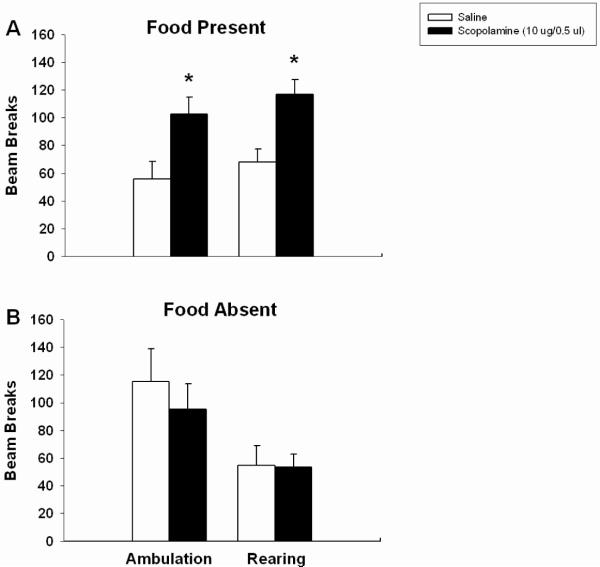
Figure 4.
Effects of scopolamine on ambulation and rearing in the presence and absence of food. Scopolamine-treated rats ambulated and reared significantly more times than saline controls (A). No increase in motor activity was observed in an environment without food association (B). Error bars depict one SEM. (* p ≤ 0.05, significantly different from saline)