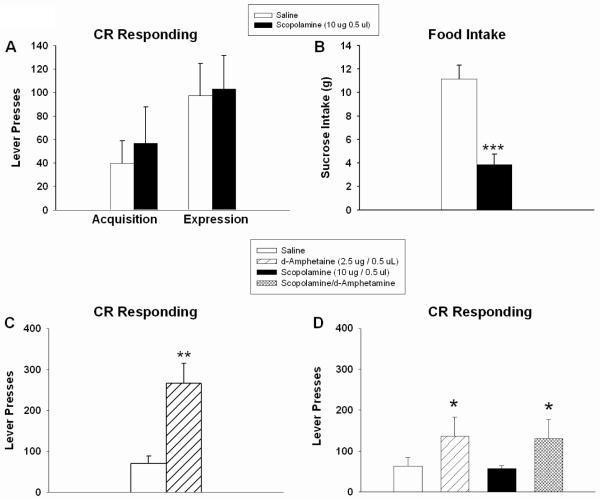
Figure 6.
Intra-Acb scopolamine (10 μg/ 0.5 ul) had no effect on CR acquisition or expression of responding for a food-associated cue (A). Sucrose pellet intake was significantly decreased 3 h following intra-Acb scopolamine (B). As shown in (C), CR responding was significantly increased following d-amphetamine infusion (2.5 ug / 0.5 ul) in the same set of rats used in (A) and (B). A different set of rats received a saline or scopolamine pretreatment followed by saline or d-amphetamine intra-Acb infusion. Amphetamine treatment significantly augmented CR responding, but scopolamine pretreatment had no effect on d-amphetamine potentiated responding (D). Error bars depict one SEM. (* p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≥ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, significantly different from saline).