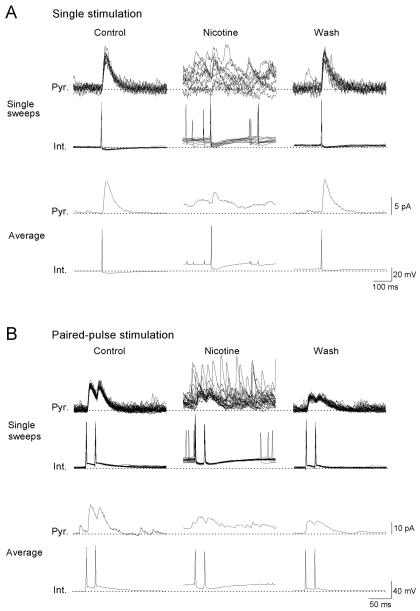
Figure 7. Nicotine causes tonic and phasic inhibitions at synapses between interneurons in the stratum oriens/alveus and pyramidal cells.
A dual whole-cell recording from a current-clamped interneuron and a voltage-clamped pyramidal cell at 0 mV was carried out. Trains of single (A) or paired spikes at the 20 ms interval (B) in the interneuron (Int.) evoked uIPSCs in the pyramidal cell (Pyr.). Ten superimposed traces and averaged traces recorded in the absence (Control) and presence of nicotine (Nicotine) and 10 min after washout of nicotine (Wash) are shown. Bath application of nicotine (10 μM) increased the frequency of sIPSCs and simultaneously depressed evoked uIPSCs. (A, B, Nicotine). Note that nicotine also caused a large shift of the baseline current during the nicotine-induced increase in the frequency of sIPSCs, perhaps due to the summation of nicotine-induced sIPSCs. The broken lines indicate the baseline potential and current in the control condition.