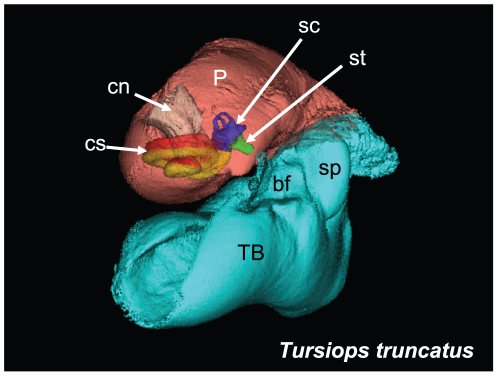
Figure 12. Anterior view of the left TPC from the second specimen of Tursiops truncatus.
The accessory ossicle of the tympanic bone (TB) has been removed to more clearly demonstrate the relative position of the cochlear spiral (cs), the semicircular canals (sc), and the cochlear nerve (cn) or eighth nerve, all contained within the periotic (P) bone. The scala vestibuli (yellow) and scala tympani (red), components of the cochlear spiral, are shown in relationship to the semicircular canals (blue), the stapes (green), the (TB) tympanic bone (cyan) and the (P) periotic (salmon). Careful inspection of the stapes (st), near the tip of the white arrow, reveals a small dimple that represents the stapedial foramen. The floor of the medial sulcus of the mallear ridge, the “ear trumpet” or “bony funnel” (bf), which receives the (cone-shaped) dorsal branch of the mandibular fat body, is also shown in this view.