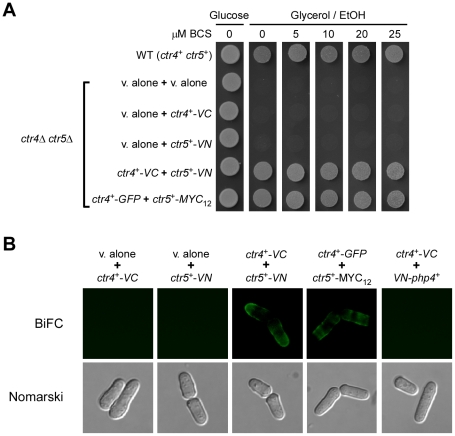
Figure 2. Co-expression of Ctr4-VC and Ctr5-VN functionally complements the respiratory deficiency of a ctr4Δ ctr5Δ mutant and produces a BiFC signal at the plasma membrane.
A, S. pombe cells harboring a ctr4Δ ctr5Δ double deletion were transformed with empty vectors (v. alone), a vector alone (v. alone) and ctr4+-VC, a vector alone and ctr5+-VN, ctr4+-VC and ctr5+-VN, or ctr4+-GFP and ctr5+-MYC12. Cultures were spotted onto YES media containing glucose or glycerol/ethanol (EtOH) and BCS (0, 5, 10, 20 and 25 µM). WT, isogenic wild-type (WT) strain FY435 (ctr4+ ctr5+). B, BiFC signal of Ctr4-VC and Ctr5-VN fusion proteins at the plasma membrane. Yeast cells disrupted for ctr4+ and ctr5+ that expressed individually, or in combination, the indicated tagged genes were grown in EMM medium containing BCS (100 µM) and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. As a positive control, co-expression of the Ctr4-GFP and Ctr5-Myc12 fusion proteins allowed Ctr4-GFP detection in the plasma membrane. As an additional proof of the specificity of the BiFC, no Venus-associated fluorescence was detected when the unrelated ctr4+-VC and VN-php4+ fusion alleles were co-expressed together. Cell morphology was examined through Nomarski optics.