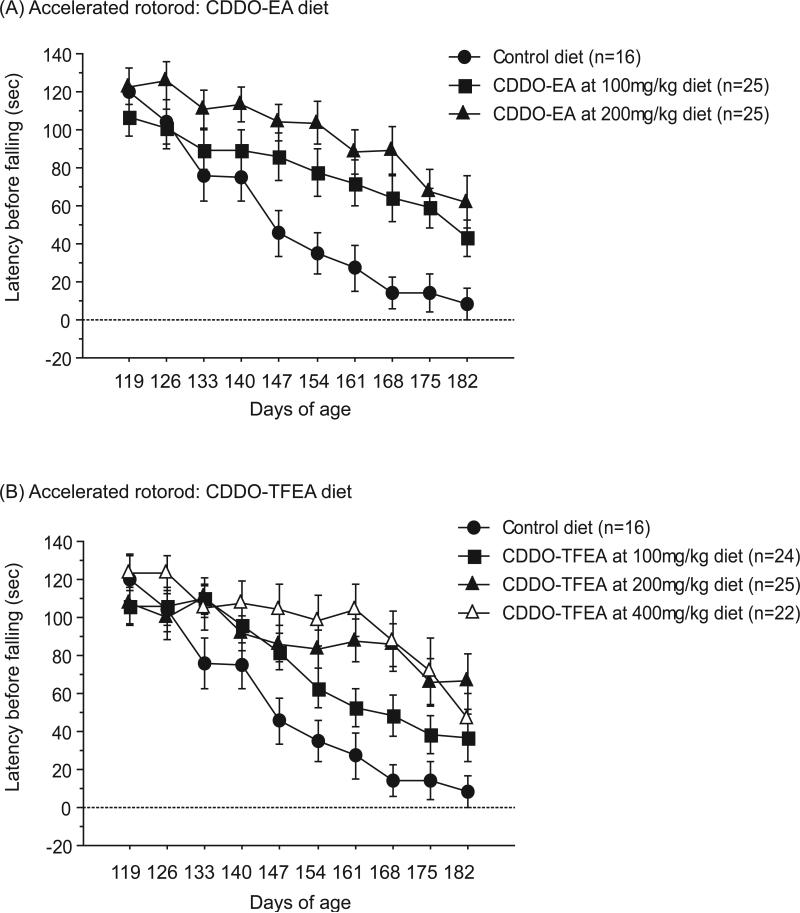
Figure 1. CDDO-ethyl amide (CDDO-EA) and CDDO-trifluoroethyl amide (CDDO-TFEA) improved motor performance in N171-82Q mice.
(A) Latency to fall during rotorod trials of N171-82Q mice treated with control diet, CDDO-EA at 100mg/kg diet and 200mg/kg diet. Data were expressed as means and standard errors. N171-82Q mice treated with CDDO-EA 100mg/kg diet and CDDO-EA 200mg/kg diet both showed significantly improved motor coordination compared to N171-82Q mice fed with control diet (p=0.04, p=0.0006). (B) Latency to fall during rotorod trials of N171-82Q mice treated with control diet, CDDO-TFEA at 100mg/kg diet, 200mg/kg diet and 400mg/kg diet. Data were expressed as means and standard errors. N171-82Q mice treated with CDDO-TFEA at 200mg/kg diet and CDDO-TFEA 400mg/kg diet both showed significantly improved motor coordination compared to N171-82Q mice fed control diet (p=0.005, p=0.0007).