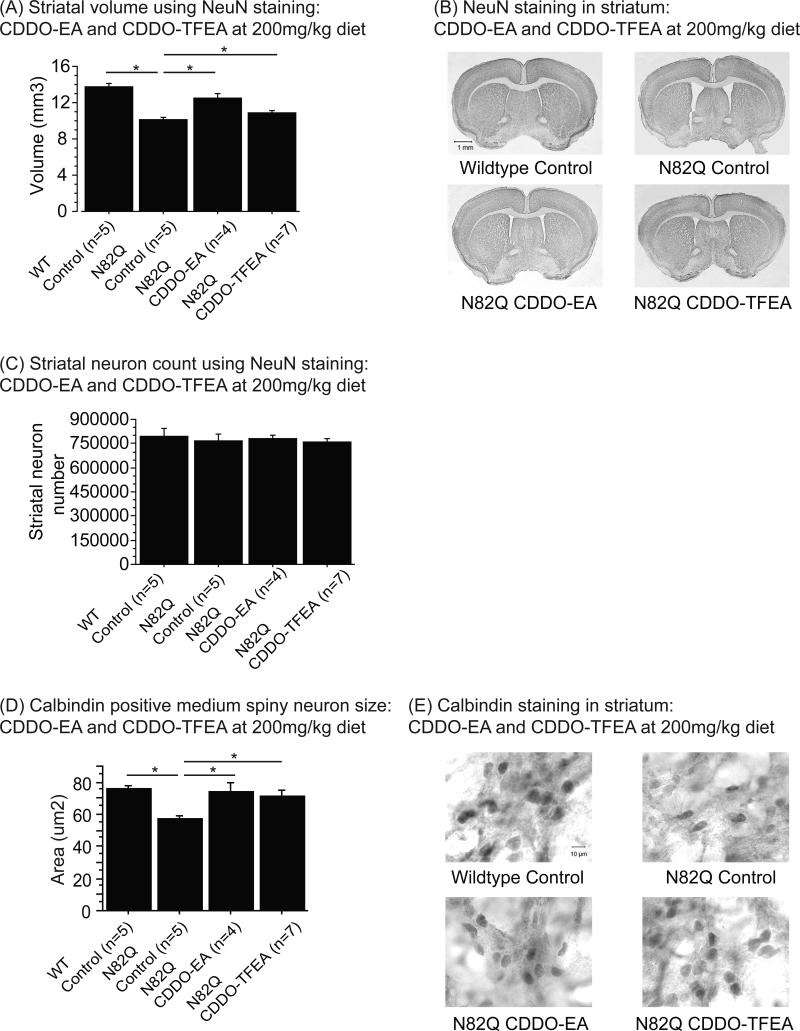
Figure 3. CDDO-ethyl amide (CDDO-EA) and CDDO-trifluoroethyl amide (CDDO-TFEA) attenuated striatal atrophy and reduction of medium spiny neuron size in N171-82Q mice.
(A) Striatal volume of NeuN labeled tissues of N171-82Q mice treated with control diet, CDDO-EA and CDDO-TFEA at 200mg/kg diet. Data were expressed as means and standard errors. (B) Photographs of brain sections labeled with NeuN antibody.
N171-82Q mice fed control diet showed a significant reduction in striatal volume compared to wildtype mice fed control diet (p<0.0001). However, treatment with both CDDO-EA and CDDO-TFEA significantly increased striatal volume in N171-82Q mice compared to N171-82Q mice fed control diet (p<0.0001, p=0.002).
(C) Striatal neuron count in NeuN labeled tissues of N171-82Q mice treated with control diet, CDDO-EA and CDDO-TFEA at 200mg/kg diet. Data were expressed as means and standard errors. There was no difference in striatal neuron count between any of the groups.
(D) Calbindin positive medium spiny neuron size of N171-82Q mice treated with control diet, CDDO-EA and CDDO-TFEA at 200mg/kg diet. Data were expressed as means and standard errors. (E) Photographs of brain sections labeled with calbindin antibody. N171-82Q mice fed control diet showed a significant reduction in medium spiny neuron size compared to wildtype mice fed control diet (p=0.001). N171-82Q mice treated with CDDO-EA and CDDO-TFEA showed significantly larger medium spiny neuron size compared to N171-82Q mice fed control diet (p=0.004, p=0.006).