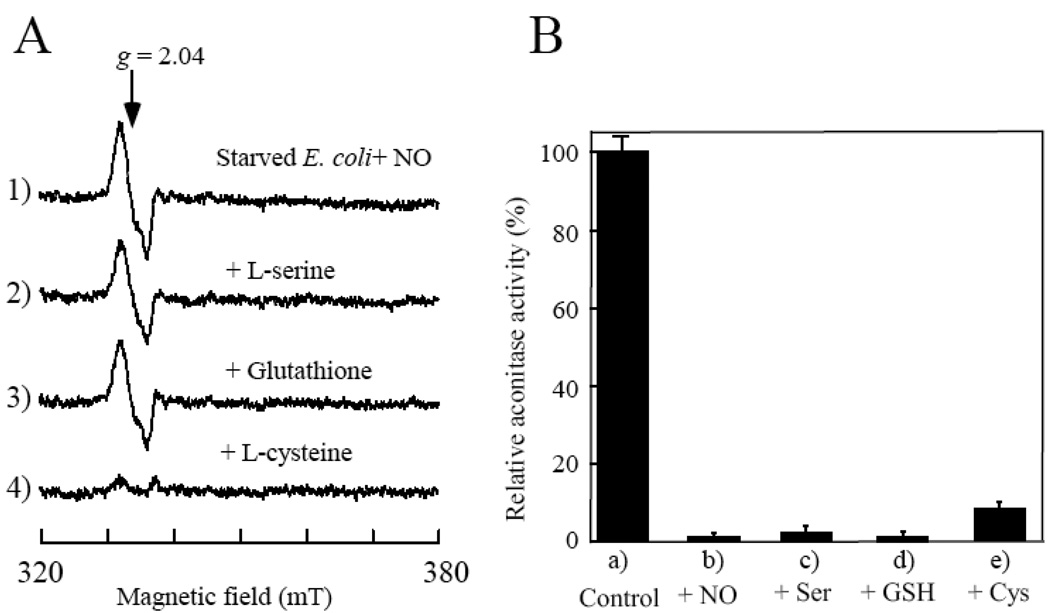
Figure 2. L-cysteine mediates decomposition of the protein-bound DNICs in the starved E. coli cells under aerobic conditions.
A), L-cysteine has a unique activity in decomposing the protein-bound DNICs in the starved E. coli cells under aerobic conditions. The NO-exposed starved E. coli cells (spectrum 1) were incubated in the M9 minimal medium (without glucose) supplemented with L-serine (1 mM) (spectrum 2), reduced glutathione (1 mM) (spectrum 3), or L-cysteine (1 mM) (spectrum 4) at 37°C for 60 min under aerobic conditions. B), relative aconitase activity in the cell extracts prepared from a), untreated starved E. coli cells; b), the NO-exposed starved E. coli cells; c), d), and e), the NO-exposed starved E. coli cells re-incubated aerobically at 37°C for 60 min in the M9 minimal medium supplemented with L-serine (Ser) (1 mM), reduced glutathione (GSH) (1 mM), or L-cysteine (Cys) (1 mM), respectively. The data are the averages from three independent experiments.