Figure 2. Laser machining process.
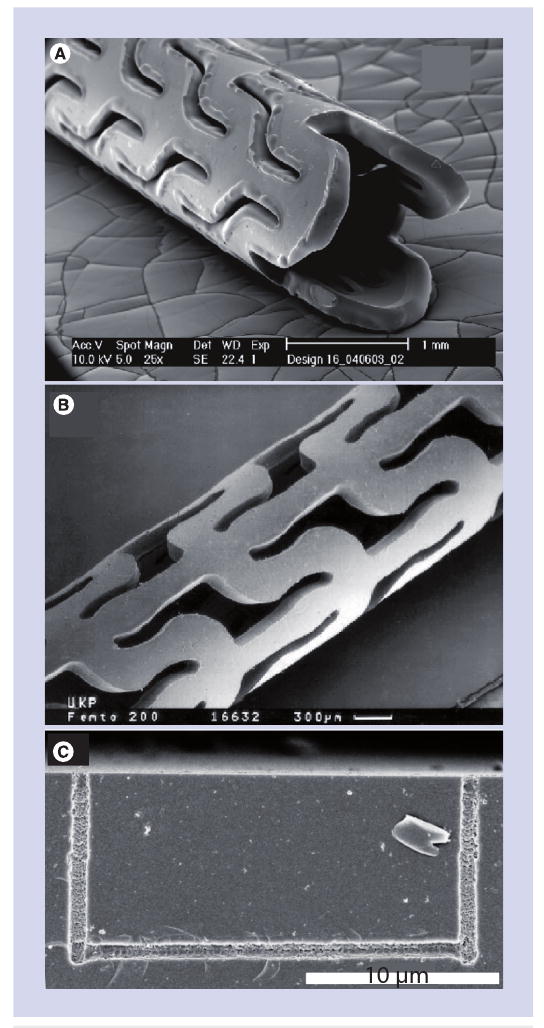
(A) Poly(l-lactide) stent machined using a continuous wave CO2 laser. (B) Poly(l-lactide) stent machined using a femtosecond laser. (C) Glass microfluidic device containing a nano-scale channel machined on the interior of the structure using a femtosecond laser.
(A) Reprinted from [64] with permission from ASME.
(B) Reprinted from [55] with kind permission of Springer, Science+Business Media © 1999.
(C) Reprinted with permission from [1]. © 2005 American Chemical Society.
