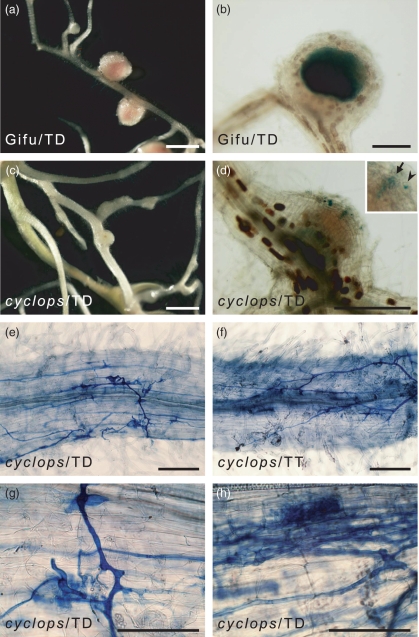
Figure 3.
Complementation of rhizobial infection phenotypes and mycorrhization phenotypes of cyclops mutant by CCaMKT265D or wt-CCaMK transformation. Symbiotic phenotypes of transformed plants were observed 4 weeks after inoculation with lacZ-labelled Mesorhizobium loti (a–d) or Glomus intraradices (e–h). (a, c) Mature nodules on the roots of wild-type/CCaMKT265D (Gifu/TD) and bump-like structures on the roots of cyclops-4/CCaMKT265D (cyclops/TD) were formed. Scale bars are 1 mm. (b, d) Rhizobial infection was confirmed by lacZ staining. Effective nodules with rhizobial infection were formed on the roots of Gifu/TD (b), but rhizobial infection was aborted at the epidermis on bump-like structures on the roots of cyclops/TD (d). The inset shows magnified view of the aborted infection thread (arrow) and the micro-colony (arrowhead). Scale bars are 500 μm. (e–h) Roots of cyclops/TD were filled with arbuscules only occasionally (h), fungal invasion was aborted in the epidermis and only running hyphae (e) and swollen appressoria (g) were observed in the roots of cyclops-4/TD, as well as cyclops-4/wt-CCaMK (f). Scale bars are 200 μm (e,f) and 100 μm (g, h).