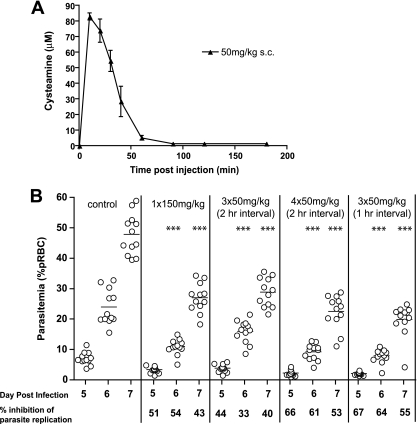
FIG. 2.
Effect of cysteamine dosing used for treatment of cystinosis on replication of Plasmodium chabaudi in vivo. (A) The plasma levels of cysteamine-free base (measured by HPLC) following subcutaneous (s.c.) injection (50 mg/kg) were measured in 3 mice and used to calculate Cmax and AUC pharmacokinetic parameters (see text). Error bars indicate standard deviation from the mean. (B) A/J female mice were infected with P. chabaudi (105 pRBC i.v.) and treated daily with cysteamine (s.c.) from day −1 to day 10, with the indicated dosing: 1 × 150 mg/kg, 3 × 50 mg/kg, or 4 × 50 mg/kg, given at 1 or 2 h intervals. Blood parasitemia was monitored on days 5, 6, and 7 and is plotted. The % inhibition of parasite replication was calculated by comparison to the blood parasitemia measured in PBS-treated controls and is indicated below the graphs. Each dot represents a mouse. Levels of statistical significance are represented by asterisks; ***, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.05 (compared to PBS control group).