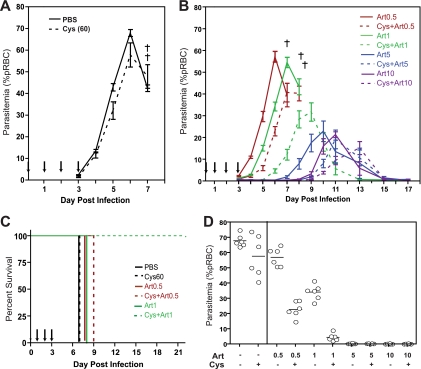
FIG. 5.
Effect of cysteamine and artesunate combinations on progression and resolution of P. chabaudi infection in vivo. Groups (n = 6) of female A/J mice were infected with P. chabaudi (106 pRBC, i.v.) and treated for 4 days (days 0, 1, 2, and 3) with PBS (A), cysteamine (60 mg/kg, A), or cysteamine (60 mg/kg) combined with increasing doses of artesunate (0.5, 1.0, 5, or 10 mg/kg) (B), all given i.p. Blood parasitemia was measured daily up to day 20 (expressed as percentage of pRBC), and death was recorded (indicated by a cross). Solid and dashed lines represent mice receiving artesunate doses alone or in combination with cysteamine, respectively; artesunate doses are depicted by different color groups, as indicated. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean, and arrows represent drug treatment days. (C) Kaplan-Meier survival plot for experimental treatment groups for which lethality was observed. Color codes and dashed versus solid lines are as described for panel B. (D) Parasitemia levels at day 6 postinfection for all experimental groups are shown, with each dot representing a mouse. Mean levels are shown as bars.