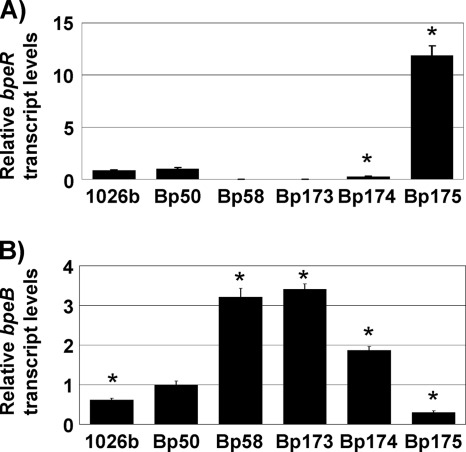
FIG. 1.
bpeR and bpeB transcript levels in wild-type, deletion, and complemented strains. mRNA levels in LB-grown mid-log cultures of the indicated strains were determined with bpeR- and bpeB-specific primer sets. Data were normalized using the 23S rRNA gene as the housekeeping control. (A) bpeR transcript levels relative to those found in Bp50 were determined for the following strains: wild-type 1026b, its Δ(amrRAB-oprA) derivative Bp50, and its Δ(amrRAB-oprA) ΔbpeR derivative Bp58. Bp173, Bp174, and Bp175 are Bp58 mutants containing an empty mini-Tn7 vector, a mini-Tn7 element expressing bpeR from its own promoter, and a mini-Tn7 element expressing bpeR from the constitutive P1 promoter, respectively. Asterisks mark bpeR mRNA levels that are statistically significantly different (according to t test) from those detected in 1026b. (B) bpeB transcript levels in the same strains as above relative to the levels found in Bp50. Experiments were performed in triplicate. Error bars represent standard deviations. Asterisks mark bpeB mRNA levels that are statistically significantly different (according to t test) from those detected in Bp50.