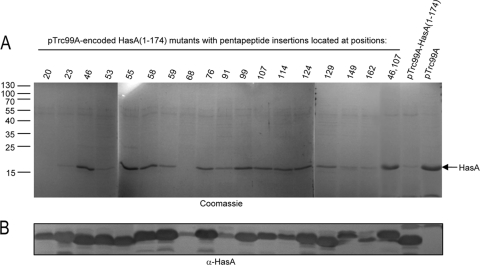
FIG. 3.
Effects of HasA(1-174) mutant forms carrying pentapeptide insertions on wild-type HasA secretion. (A) Wild-type HasA was expressed from pAM-HasISRADE; HasA(1-174) and derivative mutant proteins carrying pentapeptide insertions at various positions were under the control the IPTG-inducible promoter Ptrc in pTrc99A. Cultures of E. coli strain MC4100 were first induced for type 1 secretion with 0.2 mM 2,2′-dipyridyl for 1 h. Cultures were then grown in the presence of 0.5 mM IPTG for 3 h to induce the expression of mutant HasA(1-174) proteins. Following centrifugation of culture aliquots, proteins in the supernatants were precipitated with trichloroacetic acid, separated by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by Coomassie blue staining. (B) Cultures of MC4100 with pTrc99A-HasA(1-174) were induced with IPTG. Cells were harvested by centrifugation, followed by suspension in BugBuster reagent at room temperature and Benzonase treatment according to the manufacturer's instructions. Insoluble proteins and cell debris were removed by centrifugation. Proteins released in the soluble fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and detected with anti-HasA polyclonal antiserum. Loaded samples were normalized to an OD600 of 0.2. HasA(1-174) and HasA mutant proteins showed different migrations on SDS-PAGE due to the nature of the inserted amino acids, as previously reported (31). The molecular masses of the markers (kilodaltons) are indicated at the left.