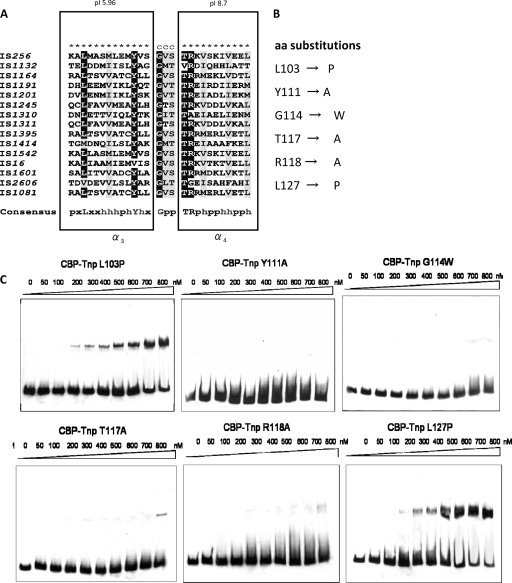
FIG. 3.
Analysis of a putative HTH DNA-binding motif of the IS256 transposase. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment (25) of the putative DNA-binding region of IS256 (aa 100 to 130) and other bacterial members of the IS256 family. ★, α-helix; C, coiled region. Rectangles mark the predicted α-helices α3 and α4, respectively. Highly conserved and conserved residues are highlighted in black and gray, respectively. In the consensus sequence, “x,” “p,” and “h” indicate variable, polar, and hydrophobic amino acid residues, respectively. (B) Amino acid exchanges of highly conserved and conserved residues within the putative HTH motif of the CBP-Tnp protein. (C) EMSAs with 15.5 nM IS terminus (right)-specific DNA as substrate and increasing amounts of the altered CBP-Tnp proteins described in panels A and B. Binding assays were performed in the presence of 50 μg of poly(dI-dC) ml−1 as a nonspecific competitor, and molar DNA/protein ratios ranged from 1:3 (50 nM protein) to 1:52 (800 nM protein), respectively.