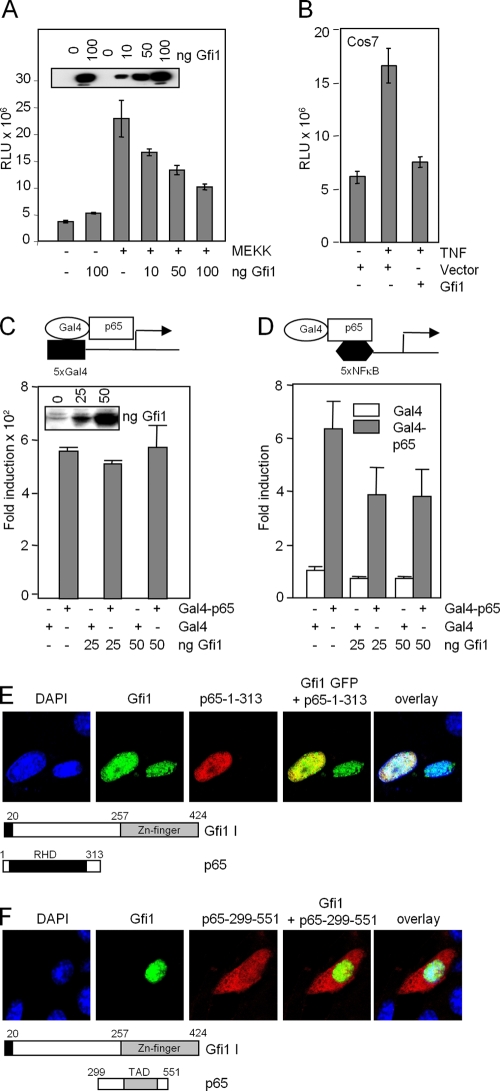
FIG. 8.
Gfi1 represses NF-κB transcriptional activity and binds to the p65 Rel homology domain. (A and B) Reporter gene assays with RK13 cells (A) or COS7 cells (B) with a luciferase vector containing 5xNF-κB binding sites. Activation of NF-κB was achieved by cotransfecting the expression constructs for MAP kinase MEKK (A) or by treating the cells with TNF that activates p65 (B). Expression levels of Gfi1 are shown in the inset in panel A. RLU, relative light units. (C and D) Gfi1 interferes with DNA binding and not transcriptional transactivation of p65. Reporter gene assays were performed with NIH 3T3 cells transfected with combinations of expression constructs encoding Gal4 (white bar) or Gal4-p65 (gray bar) fusion proteins, increasing amounts of Flag-Gfi1, and either a 5xGal4 reporter (C) or a 5xNF-κB reporter (D). All data are representative of three independent experiments. (E) Coexpression of the indicated p65 mutants lack-ing either the TAD domain or the Rel homology domain (RHD) with full-length Gfi1. Interaction between Gfi1 and the RHD part of p65 is clearly observed. (F) The p65 mutant containing only the TAD remains in the cytoplasm, indicating that it lacks the ability to interact with Gfi1.