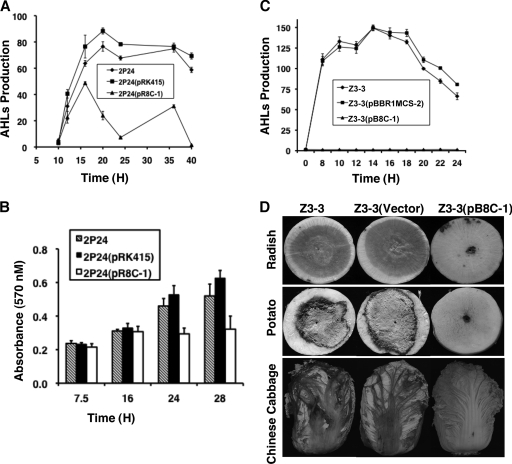
FIG. 7.
Effect of AidH on phenotypes of Pseudomonas fluorescens 2P24 and P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum. Vectors or their derivatives expressing AidH were introduced into Pseudomonas fluorescens 2P24 and P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum, and the resulting strains were tested for extracellular AHL accumulation (A and C), biofilm formation (B), and pathogenicity (D). AHLs produced by bacterial strains were evaluated for their abilities to activate traG on A. tumefaciens biosensor strain NTL4(pZLR4), measured by the expression of a TraR-dependent LacZ fusion. The activity of β-galactosidase is expressed in Miller units. The formation of biofilm in Eppendorf tubes was evaluated by crystal violet staining as described previously by Wei and Zhang (56). Error bars indicate standard deviations of data from three experiments. (D) Radish, potato, and Chinese cabbage were inoculated with 5 μl of bacterial culture (2 × 109 CFU/ml) of Z3-3, Z3-3(pBBR1MCS-2) (vector), and Z3-3(pB8C-1), respectively. The development of disease symptoms was documented by photographing the inoculated plant tissues 48 h (radish and potato) or 5 days (Chinese cabbage) after inoculation. Similar results were obtained in multiple independent experiments, and images shown are representative of one experiment.