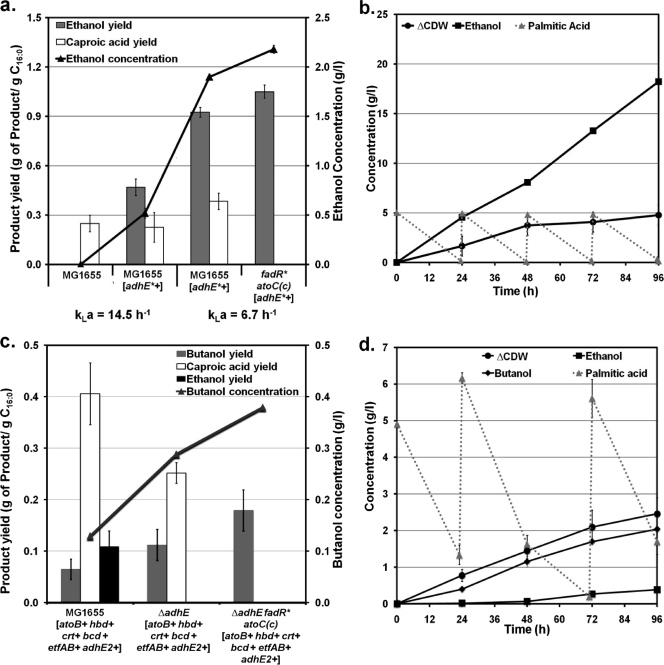
FIG. 2.
Engineering E. coli for the production of ethanol (a and b) and butanol (c and d) from fatty acids. Values represent the means and standard deviations for triplicate cultures. Gene overexpression and deletion are indicated by + and Δ, respectively, next to the corresponding gene or operon. Details about the pathways can be found in Fig. 1. (a) Ethanol concentration (line) and ethanol and caproic acid yields (bars) for 72-hour cultures of wild-type MG1655 and strains containing engineered pathways for ethanol production (oxygen-tolerant acetaldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase, adhE*) and efficient catabolism of FAs [fadR* atoC(Con)]. kLa, volumetric oxygen transfer coefficient (h−1). (b) Fermentation profile for strain MG1655 ΔadhE fadR*atoC(Con) [adhE*+] in minimal medium with 5 g/liter palmitic acid (C16:0) and using a kLa of 6.7 h−1. Additions of palmitic acid (5 g/liter each) were made every 24 h. ΔCDW, increase in cell dry weight with respect to the initial value. (c) Butanol concentration (line) and butanol, ethanol, and caproic acid yields (bars) for 72-hour cultures of strains engineered by (i) expression of the C. acetobutylicum pathway for the synthesis of butanol from acetoacetyl-CoA (hbd, crt, bcd, etfAB, and adhE2), (ii) overexpression of the E. coli acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase (atoB) for the conversion of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl-CoA, (iii) elimination of the E. coli native ethanol pathway (adhE), and (iv) engineering the β-oxidation pathway for efficient catabolism of FAs [fadR*atoC(Con)]. A kLa of 6.7 h−1 was used. (d) Fermentation profile for strain MG1655 ΔadhE fadR*atoC(Con) [atoB+ hbd+ crt+ bcd+ etfAB+ adhE2+] in minimal medium with 5 g/liter palmitic acid (C16:0) and a kLa of 6.7 h−1. Two additions of palmitic acid (5 g/liter each) were made at 24 and 72 h. ΔCDW, increase in cell dry weight with respect to initial value.