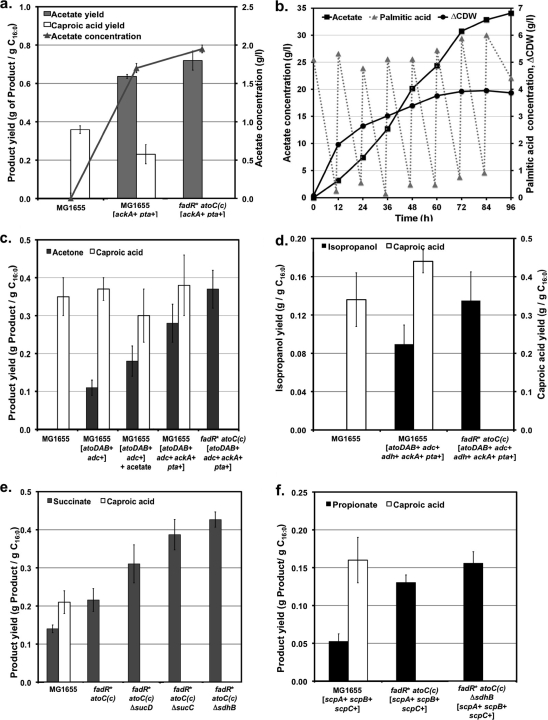
FIG. 3.
Production of acetate (a and b), acetone (c), isopropanol (d), succinate (e), and propionate (f) from FAs in engineered E. coli strains. Details about the engineered pathways are shown in Fig. 1. Gene overexpression and deletion are indicated by + and Δ, respectively, next to the corresponding gene or operon. A kLa of 14.5 h−1 was used in all experiments. Values represent the means and standard deviations for 72-hour triplicate cultures. (a) Acetate concentration (line) and acetate and caproic acid yields (bars) in wild-type MG1655 and recombinant strains constructed by overexpressing the native phopshoacetyltransferase (pta)-acetate kinase (ackA) pathway for conversion of acetyl-CoA to acetate and modifying the β-oxidation pathway for efficient catabolism of FAs [fadR*atoC(Con)]. (b) Fermentation profile for strain MG1655 fadR*atoC(Con) [ackA+ pta+] in minimal medium with 5 g/liter palmitic acid (C16:0). Additions of palmitic acid (5 g/liter each) were made every 12 h. ΔCDW, increase in cell dry weight with respect to initial value. (c) Acetone and caproic acid yields in strains constructed by overexpressing E. coli acetyl-CoA and acetoacetyl-CoA transferases (atoDAB) and C. acetobutylicum acetoacetate decarboxylase (adc) along with amplification of the native acetate pathway (ackA-pta). These modifications were implemented in wild-type MG1655 and the fadR*atoC(Con) derivative. (d) Isopropanol and caproic acid yields in strains engineered for acetone production and overexpressing a secondary alcohol dehydrogenase from C. butyricum (adh), which converts acetone to isopropanol. (e) Effects of fadR*atoC(Con) genotype and deletions of genes encoding TCA cycle enzymes on succinate and caproic acid yields. (f) Propionate and caproic acid yields in strains overexpressing a metabolic cycle that catalyzes the decarboxylation of succinate to propionate (scpA, scpB, scpC). The effect of amplification of this cycle, along with the deletion of succinate dehydrogenase (ΔsdhB), was evaluated in wild-type MG1655 and the fadR*atoC(Con) derivative.