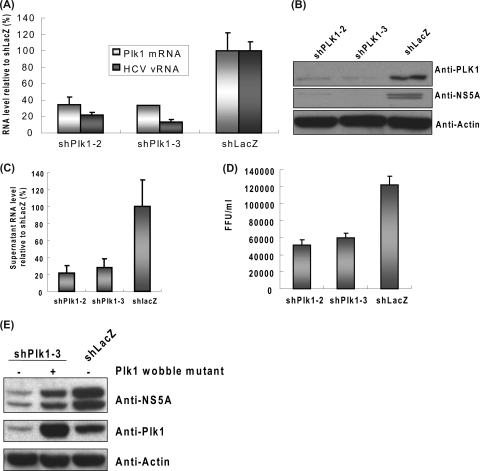
FIG. 2.
Depletion of Plk1 decreased HCV replication and virion production in infectious HCVcc system. (A to D) shPlk1-2 and shPlk1-3 were transduced into Huh-7.5 cells, and the transduced cells were selected with puromycin for 2 days. Cells were then subcultured and infected with JC1 virus (MOI of 1). Three days after infection, cells were collected and analyzed with quantitative RT-PCR (A) (normalized to GAPDH RNA; mean ± standard deviation; n = 3) or Western blotting (B). Supernatant was collected for RNA extraction for quantitative PCR (C) and viral titer determination (D). The viral RNA was normalized by the input volume of supernatant (mean ± standard deviation; n = 3). In panel D the serially diluted supernatant from the JC1-infected shPlk1/shLacZ knocked down cells was applied to Huh-7.5 cells in 96-well plates. The number of focus forming units (FFU) was calculated at day 3 postinfection by staining of core protein (mean ± standard deviation; n = 3). (E) The lentiviruses carrying the rescue (pLKO_AS3w.neo-Plk1-3R)- or control (pLKO_AS3w.neo)-expressing vector were transduced in Huh-7.5 cells to establish stable cell lines and then infected with shPlk1-3 or shLacZ viruses as indicated. The subsequent HCV infection was as described above.