FIG. 2.
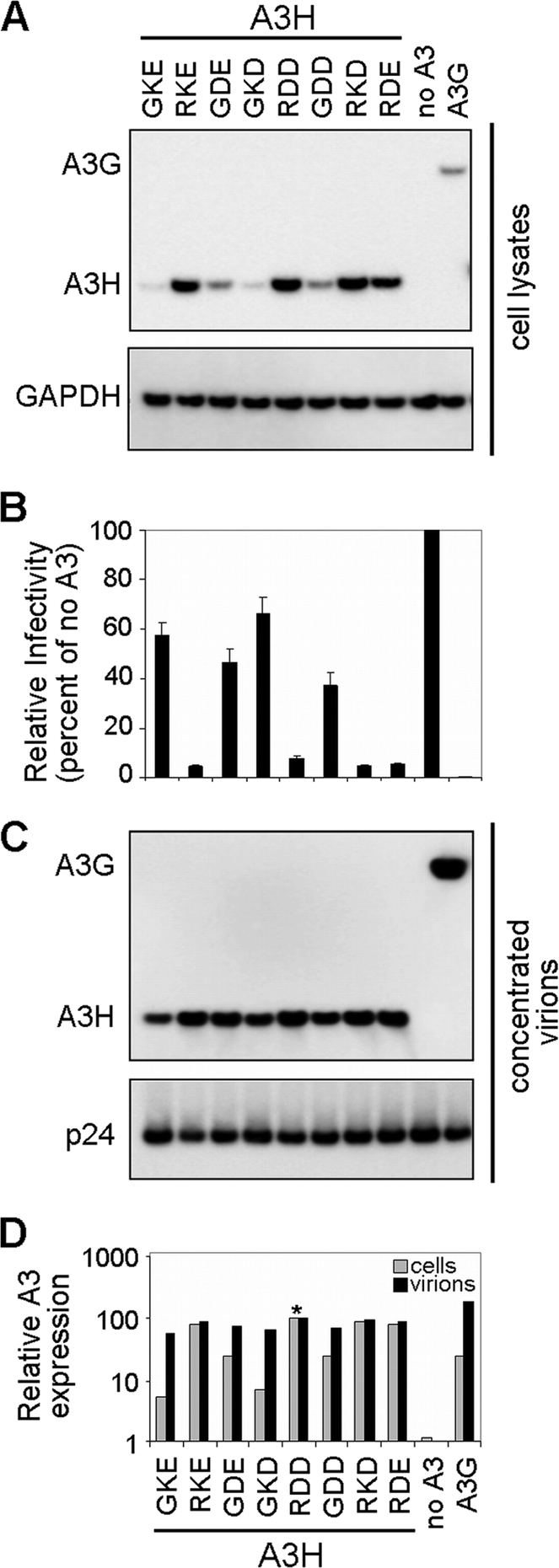
Expression, antiviral activity, and virion incorporation of A3H variants (hapI-GKE, hapII-RDD, and mutants) and A3G. (A) HIV-1 ΔVif viruses (500 ng) were produced by transfection in the presence of eight different APOBEC3H variants (100 ng), empty pTR600 plasmid (100 ng), or APOBEC3G (100 ng). A3H and A3G expression levels (anti-FLAG) were assessed by Western blotting of transfected HEK 293T cell lysates. Detection of GAPDH served as a protein loading control. Data from one representative experiment of three are shown. (B) Viral infectivity was assessed by infection of TZM-bl reporter cells. Results were normalized by using the no-APOBEC3 controls as a reference and are plotted as the percent relative mean infectivity. TZM-bl infections were performed in triplicates, and results from three independent transfection experiments are shown. (C) Viral stocks were concentrated through a 20% sucrose cushion and separated by SDS-PAGE. Virion incorporation of A3H and A3G was detected by Western blotting using an anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody. HIV-1 p24 was probed by using anti-HIV serum. (D) A3H and A3G cellular expression and virion incorporation were quantified by using the Fujifilm Intelligent Lightbox LAS-3000 instrument and Image Reader LAS-3000 software. Signals were normalized by setting both A3H hapII-RDD expression levels at 100% (indicated by an asterisk).
