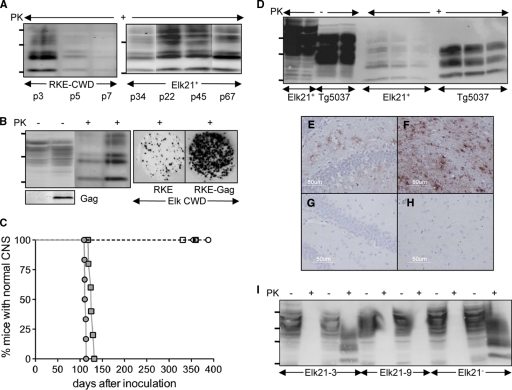
FIG. 1.
Characterization of cell cultures for studying CWD prions. (A) Western blots showing accumulation of CerPrPSc in RKE cells challenged with CWD brain homogenates from elk isolate 012-09442, passaged in Tg5037 mice (RKE-CWD) (left) and Elk21+ cells (right). Passage numbers (p) of cell cultures are indicated. (B) Expression of CerPrPC and HIV-Gag and accumulation of CerPrPSc in RKE and RKE-Gag cells infected with CWD brain homogenates. Cultured cells were also analyzed by cell blotting (right). (C) Bioassay of Elk21+ cells propagating elk CWD 012-09442 prions (filled circles), elk CWD 012-09442 prions in Tg5037 mice (filled squares), uninfected RKE-Gag (open circles), Elk21− 13 passages after DS-500 treatment (open triangles), Elk21− 30 passages after DS-500 treatment (filled triangles), the Elk21-3 clone (open diamonds), and the Elk21-9 clone (open squares). (D) Western blots of CerPrPC (100 and 50 μg total protein loaded in each case) and CerPrPSc (200, 100, and 50 μg total protein loaded in each case) produced in Elk21+ cells and Tg5037 mice inoculated with Elk21+ cell extracts. (E to H) CerPrPSc deposition in the hippocampus (E and G) and thalamus (F and H) of Tg5037 mice inoculated with either Elk21+ (E and F) or uninfected RKE-Gag (G and H) cell extracts. (I) Western blots demonstrating susceptibility of Elk21-3, Elk21-9, and Elk21− to reinfection with elk CWD 012-09442 prions. For each cell line, the first two lanes show extracts from mock (phosphate-buffered saline [PBS])-infected cells, while the second two lanes show extracts from cells exposed to CWD brain homogenates. In all Western blots, samples were either PK treated (+) or untreated (−), and the positions of protein molecular mass markers at 37, 25, and 20 kDa (from top to bottom) are shown.