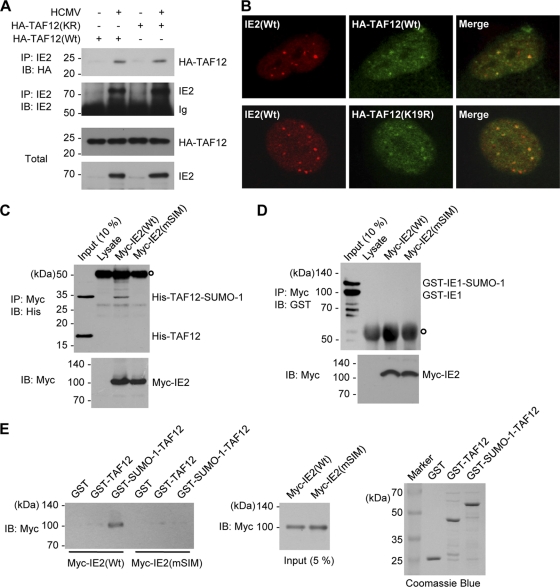
FIG. 8.
Interaction of IE2 with the SUMO-modified form of TAF12. (A) CoIP assays for IE2 and TAF12 in infected cells. HF in 100-mm-diameter dishes were first transfected with wild-type or K19R mutant TAF2 via electroporation and then infected with HCMV at an MOI of 5. At 8 h, whole-cell lysates were prepared, and CoIP assays were performed with an anti-IE2 Ab. (B) Colocalization of IE2 and TAF12 in infected cells. HF cultured in chamber slides were transfected and infected as described for panel A. Cells were fixed in cold methanol, and confocal double-label IFA was performed with anti-IE2 and anti-HA Abs. (C) In vitro interaction of IE2 with SUMO-modified TAF2 in a SIM-dependent manner. His-TAF12 and SUMO-1-modified His-TAF12 proteins, which were produced in E. coli cotransformed with plasmids expressing the SUMO conjugating enzymes (pT-E1E2-S1) (see Materials and Methods) and His-TAF12, were incubated with the control rabbit reticulocyte lysates or in vitro-translated myc-IE2(Wt) or myc-IE2(mSIM) proteins. After immunoprecipitation with an anti-myc Ab, the coprecipitated proteins were immunoblotted with an anti-His Ab (top). Ten percent (each) of the His-TAF12 proteins and myc-IE2 proteins is shown as an input control. The open circle at the top left indicates immunoglobulins. (D) An assay similar to that for which results are shown in panel C was conducted using GST-IE1 and SUMO-modified GST-IE1, which were produced in E. coli. (E) In vitro GST pulldown assays. GST, GST-TAF12, and GST-SUMO-1-TAF12 fusion proteins produced in bacteria were incubated with in vitro-translated myc-IE2(Wt) or myc-IE2(mSIM) proteins. The bound IE2 proteins were identified by immunoblotting with an anti-Myc Ab (left panel). The amounts of myc-IE2 and GST or GST fusion proteins used are shown as input controls (center and right panels).