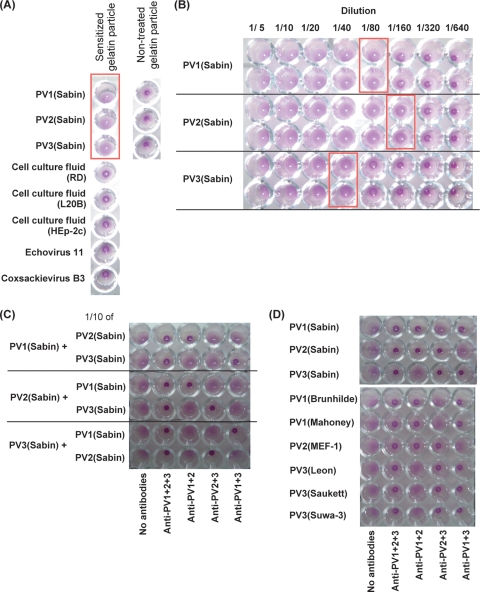
FIG. 2.
Characterization of PA method and identification of PV strains. (A) Specificity of sensitized gelatin particles for PV. The agglutination activity of gelatin particles was examined with nonpoliovirus enteroviruses (echovirus 11 and CVB3) and nontreated gelatin particles. Wells that showed agglutination are shown in a box. (B) Sensitivity of the PA method for PV(Sabin) strains. Virus solutions of PV1(Sabin), PV2(Sabin), and PV3(Sabin) (virus titers of 9.5 × 106 CCID50/μl [1.1 × 108 CCID50 in 12 μl], 6.9 × 106 CCID50/μl [8.2 × 107 CCID50 in 12 μl], and 2.9 × 106 CCID50/μl [3.5 × 107 CCID50 in 12 μl], respectively) were diluted 1/5 to 1/640 and then examined by the PA method. The detection limit of the PA method for each sample observed on the reaction plate is shown with a box. (C) Identification of mixed PV(Sabin) strains by the PA method. Virus solutions of PV1(Sabin), PV2(Sabin), and PV3(Sabin) (virus titers of 9.5 × 106 CCID50/μl [1.1 × 108 CCID50 in 12 μl], 6.9 × 106 CCID50/μl [8.2 × 107 CCID50 in 12 μl], and 2.9 × 106 CCID50/μl [3.5 × 107 CCID50 in 12 μl], respectively) were mixed with a 1/10 volume (1.2 μl) of each PV(Sabin) strain and then subjected to the PA method for identification. (D) Identification of wild-type PV strains by the PA method. Virus titers of wild-type strains examined [PV1(Brunhilde), PV1(Mahoney), PV2(MEF-1), PV3(Leon), PV3(Saukett), and PV3(Suwa-3)] were 3.2 × 106 CCID50/μl, 1.8 × 106 CCID50/μl, 1.0 × 107 CCID50/μl, 1.0 × 106 CCID50/μl, 1.0 × 106 CCID50/μl, and 5.6 × 105 CCID50/μl, respectively.