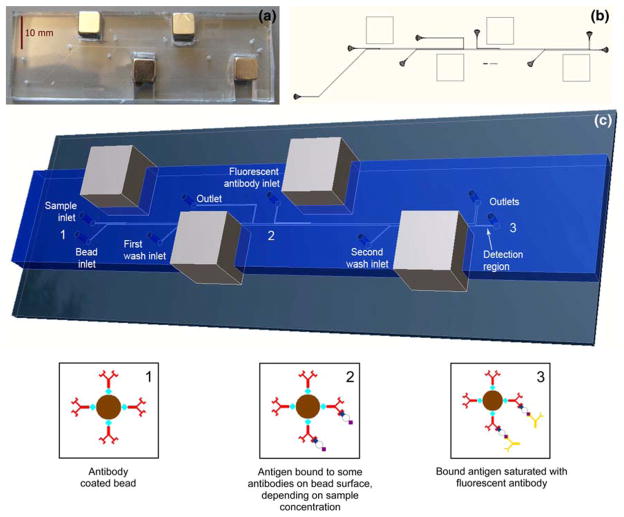
Fig. 2.
a Photograph of dual incubation microdevice. b Layout of photolithography mask for dual incubation microdevice. c Conceptual rendering from scaled 3D model of the dual incubation microimmunoassay, with bead state diagrams at device positions 1, 2, and 3. Position 1 The antibody-coated immunofluorocytometry beads are infused into the device and pulled into the sample stream. Position 2 After incubation the beads have antigen bound to them in an amount that is proportional to the sample antigen concentration. The beads are pulled into the first wash stream and transferred to the second stage, where they are pulled into the fluorescently labeled secondary antibody stream. Position 3 After the second incubation all bound antigen is bound by the fluorescent tag. Finally, the beads are pulled into the second wash stream which brings them to the detection region where fluorescence intensity detection occurs