Figure 7. Two-step activation of ANF-RGC – a model.
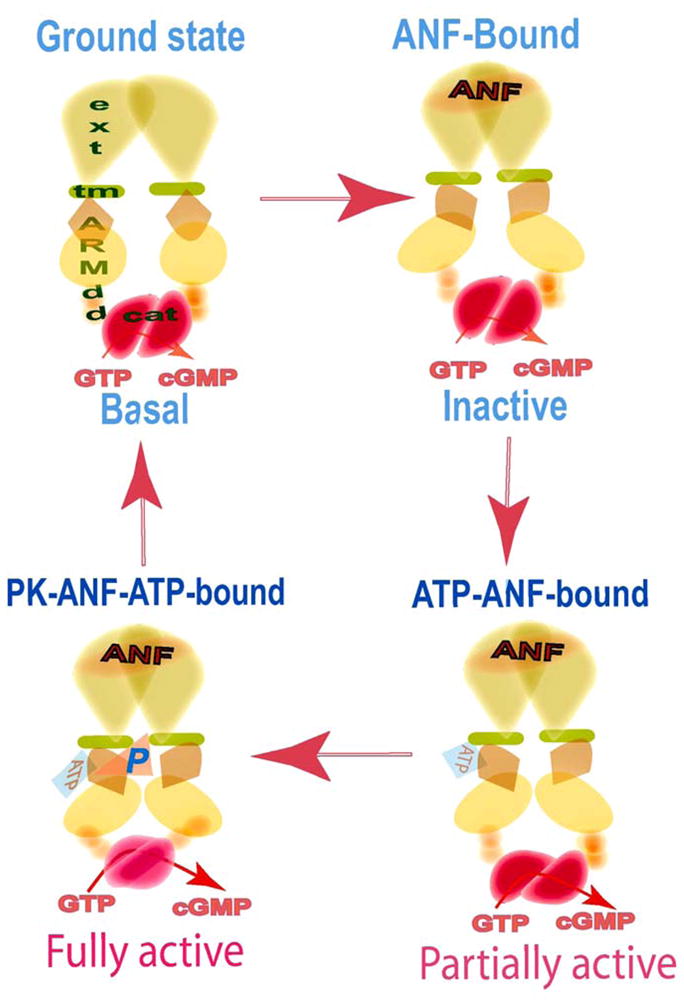
The functional domains are denoted as: ext, extracellular domain; tm, transmembrane domain; ARM, ATP regulatory domain; dd, dimerization domain; cat, catalytic domain. Ground state - In its basal state ANF-RGC exists as a dimer. ANF-Bound - The signal transduction process is initiated by binding of one molecule of ANF to the extracellular domain dimer. The binding modifies and twists the hinge juxtamembrane region and induces the structural change in ARM domain allowing it to bind ATP. The cyclase activity remains at its basal value. ATP-ANF-bound - Upon interaction with its binding pocket, ATP induces a cascade of temporal and spatial changes in the entire ARM domain. The cyclase is partially activated. PK-ANF-ATP-bound - The six serine/threonine residues within the ARM domain become phosphorylated and the 669WTAPELL675 interacts with and activates the dimeric catalytic domain. The cyclase is fully active. Note: the protein kinase (PK) involved in the phosphorylation of the ARM domain has not been identified yet.
