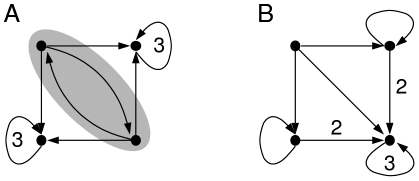
Figure 5. General iteration graph of the strongly connected symmetric component {ap1, ag}.
General iteration graph of the strongly connected symmetric component  of the reduced Mendoza & Alvarez-Buylla network
of the reduced Mendoza & Alvarez-Buylla network 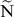 pictured in Figure 3 (a) when the states of nodes emf1 and tfl1 are both fixed to
pictured in Figure 3 (a) when the states of nodes emf1 and tfl1 are both fixed to 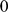 and (b) when they are both fixed to
and (b) when they are both fixed to 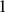 . In this graph, for the sake of clarity, we have represented
. In this graph, for the sake of clarity, we have represented  arcs with the same beginning and ending as one unique arc labelled by
arcs with the same beginning and ending as one unique arc labelled by  . The sub-graph in grey is a limit cycle of the connected component with the parallel iteration mode. It induces limit cycles 2, 3, 4 and 5 of Table 1. Note that when the state of nodes lfy and lug is fixed to
. The sub-graph in grey is a limit cycle of the connected component with the parallel iteration mode. It induces limit cycles 2, 3, 4 and 5 of Table 1. Note that when the state of nodes lfy and lug is fixed to 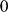 in
in 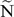 (this always becomes true after a few steps according to the proof of Proposition 1), then the connected component
(this always becomes true after a few steps according to the proof of Proposition 1), then the connected component  is free to evolve as pictured by one of these two general iteration graphs since no other nodes than emf1 and tfl1 whose states are either both
is free to evolve as pictured by one of these two general iteration graphs since no other nodes than emf1 and tfl1 whose states are either both  or both
or both 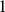 have an influence on them.
have an influence on them.