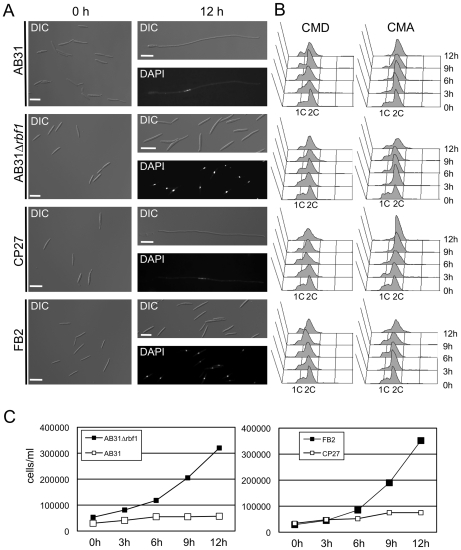
Figure 4. rbf1 is required and sufficient for b-dependent filamentation and G2 cell cycle arrest.
(A) Microscopic analysis of AB31, AB31Δrbf1, CP27 (FB2Δb::Pcrg1:rbf1) and FB2 after induction of the active bE1/bW2-heterodimer or Rbf1, respectively. Filament formation was observed 12 hours after b-induction in strain AB31 and rbf1-induction in strain CP27 (FB2Δb::Pcrg1:rbf1). In contrast, strain AB31Δrbf1 did not switch to filamentous growth and continued to grow by budding, similar to the FB2 strain that was used as negative control. Scale bar = 10 µm. (B) FACS analysis of AB31, AB31Δrbf1, CP27 (FB2Δb::Pcrg1:rbf1) and FB2 under non inducing conditions (CMD) or inducing conditions (CMA). Induction of the active bE1/bW2 combination in AB31 or induction of rbf1 in strain CP27 resulted in an enrichment of cells with a 2C content, indicative of a G2 cell cycle arrest. In AB31Δrbf1 no enrichment of cells with 2C was observed, similar to control strain FB2. (C) Measurement of cell numbers/ml in strains AB31, AB31Δrbf1, CP27 (FB2Δb::Pcrg1:rbf1) and FB2 grown in CMA for the time indicated. Strains AB31Δrbf1 and FB2 show a typical exponential growth curve, whereas strains AB31 and CP27 stopped to grow after induction of the bE1/bW2-heterodimer or rbf1, respectively, indicating a cell cycle arrest.