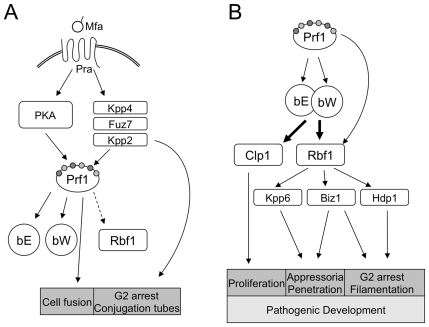
Figure 7. Key factors of a- and b-dependent development in U. maydis.
(A) Activation of the pheromone pathway after pheromone (Mfa) binding to the cognate receptor (Pra) triggers a signalling casacde via PKA and MAPK phospho-relays. Differential phosphorylation of the HMG transcription factor Prf1, in turn, leads to expression of the b-mating type locus gene bE and bW. (B) After cell fusion, sexual and pathogenic development is orchestrated by the bE/bW-heterodimer, coordinating the key players of important developmental steps: Clp1 is required for in planta proliferation; Rbf1 is the central transcriptional regulator, controlling appressoria formation and penetration of the host plant via the transcription factor Biz1 and the MAPK Kpp6, as well as filamentous growth and the G2 cell cycle arrest by concerted action of Biz1 and Hdp1.