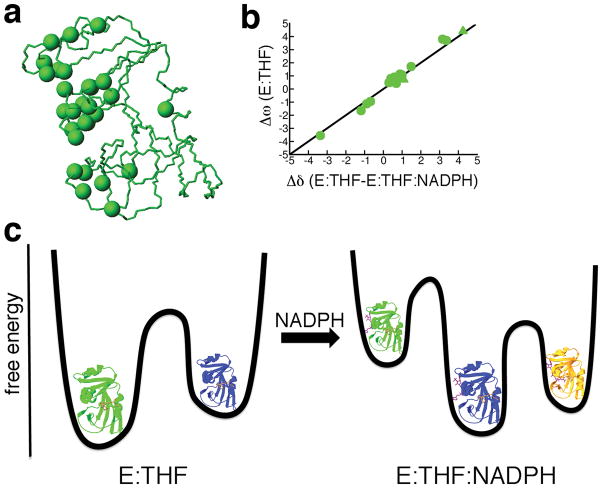
Figure 2.
Conformational selection in protein-ligand interactions observed by NMR R2 relaxation dispersion experiments. (a) Locations of conformational exchange are indicated as spheres on the structure of DHFR (pdb 1rx5). (b) A linear correlation between Δω (chemical shift difference between ground-state and higher energy conformations) from R2 relaxation dispersion experiments of the product binary complex of DHFR (enzyme bound with tetrahydrofolate (E:THF)) and Δδ from ground-state chemical shift differences between product binary and ternary (enzyme bound with tetrahydrofolate and NADPH cofactor (E:THF:NADPH)) complexes indicate that the higher energy conformation of the product binary complex is structurally similar to the ground-state of the product ternary complex (i.e. chemical shifts of the higher energy conformation of the product binary complex are similar to the chemical shifts of the ground-state conformation of the product ternary complex) (data taken from ref41). (c) The binding of the NADPH cofactor changes the free energy landscape of the enzyme. Structurally similar conformations are colored alike.