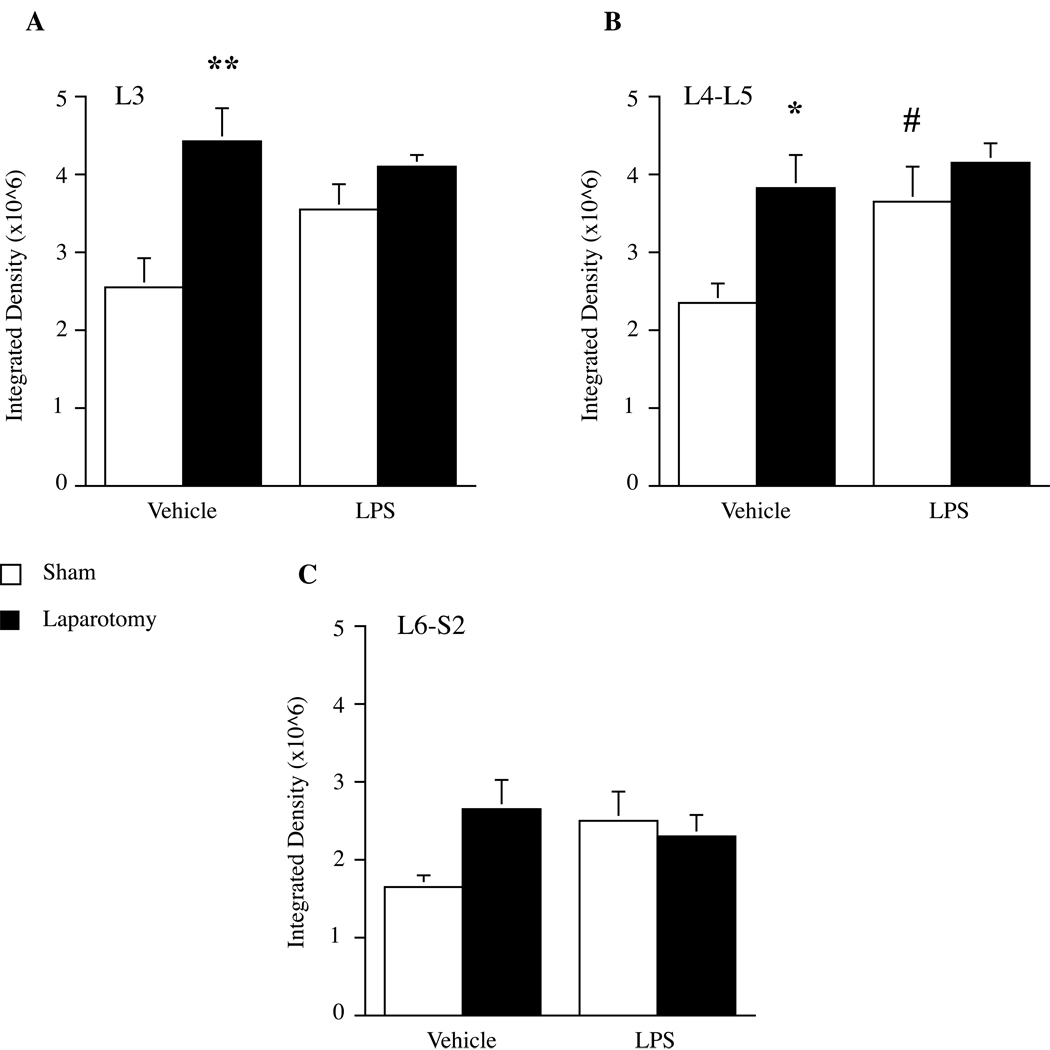
Figure 2.
Microglial activation in lumbosacral spinal cord after LPS administered two wk following laparotomy. Laparotomy (black bars) significantly increased OX-42 labeling in L3 a) and L4-L5 b). Systemic LPS induced an increase in OX-42 labeling in L4- L5 that was specific to sham-operated animals. In all areas examined, OX-42 activation was greater in laparotomy + vehicle animals compared to sham + vehicle controls. There was no interaction between laparotomy and LPS. Data represent mean integrated densities of OX-42 immunoreactivity ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.05 vs. sham + vehicle; #P < 0.05 vs. sham + vehicle.