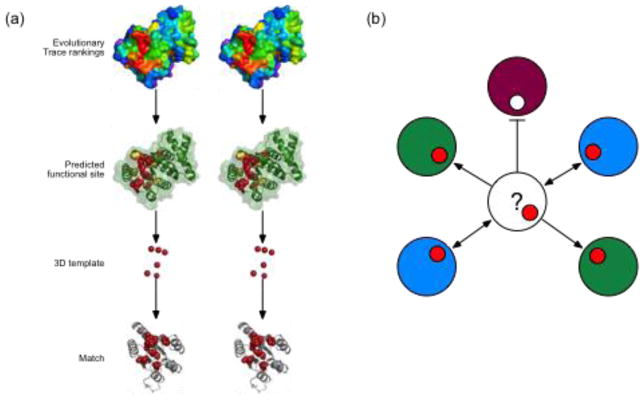
Figure 3. Structure function prediction based on evolutionary 3D templates.
(a) Evolutionary Trace rankings of residue importance for Mycobacterium tuberculosis v1626 (PDB 1sd5, chain A) are represented as a heat map of the structure’s surface (red, most important; purple, least important). Based on these rankings, the most important residues are mapped onto the structure (green ribbons) to identify a solvent-accessible cluster of 10 ET residues (red and yellow spheres). The Cα coordinates of the top six residues (red) are used as the template and searched against a database of annotated target structures. (b) A conceptual diagram of ETA heuristic filtering shows proteins as large circles, with color representing functions and templates matches as smaller circles. ETA first discards matched sites if they are not themselves evolutionary important. Red matches indicate importance and pass the filter (arrows), while white matches are unimportant and do not pass this filter (flat-headed line). ETA then examines match reciprocity, with one-way (single-headed arrows) matches rejected, and reciprocal matches (double-handed arrows) accepted. Finally, ETA requires that a predicted function achieve a vote plurality; here, after all filters are used, the two proteins with the “blue” function represent the majority of the matches. ETA would therefore predict that the query protein (question mark) has the blue function. Public ETA servers are available at http://mammoth.bcm.tmc.edu [89].