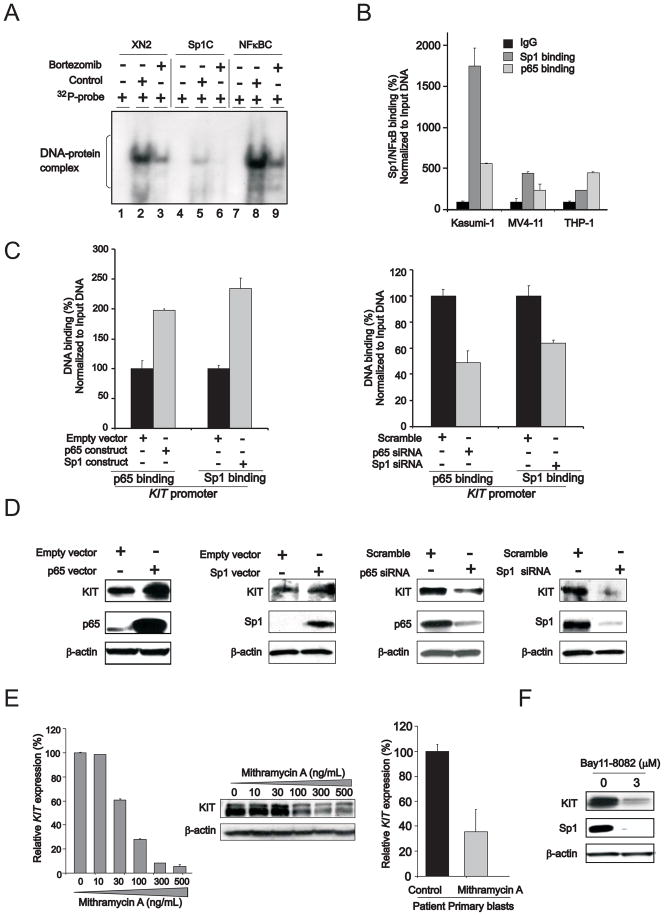
Figure 2. The regulatory role of Sp1/NFκB in KIT expression.
(A) Sp1/NFκB complex is present on KIT promoter. EMSA was performed with nuclear extracts from Kasumi-1 cells incubated with 32P-labeled double-stranded oligonucleotides containing Sp1/NFκB binding elements on the KIT promoter region from nucleotides -102/-82 (XN2) or Sp1 consensus binding sites (Sp1C) or NFκB consensus binding sites (NFκBC). Lanes 1, 4 and 7, free 32P-labeled probes; lanes 2, 5 and 8, control (untreated) cells; lanes 3, 6 and 9, bortezomib-treated cells.
(B) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays to demonstrate Sp1/NFκB on KIT gene promoter in KITmut Kasumi-1 and KITwt MV4-11 and THP1 cells (mean ± SEM).
(C) ChIP assays to show Sp1/NFκB enrichment on KIT promoter in Kasumi-1 cells transfected with NFκB or Sp1 overexpression vector (left panel) or siRNAs (right panel) (mean ± SEM).
(D) Sp1, NFκB and KIT protein expression in Kasumi-1 cells transfected with corresponding overexpression vector (left panel) or siRNA (right panel).
(E) Sp1 inhibition by mithramycin A impaired KIT RNA transcription and protein expression in Kasumi-1 cells (left and middle panels) or patient primary blasts (right panel) (mean ± SEM).
(F) NFκB inhibitor bay11-7082 (3 μM) decreased KIT expression in Kasumi-1 cells.
Data are representatives of three independent experiments. (See also Figure S2)