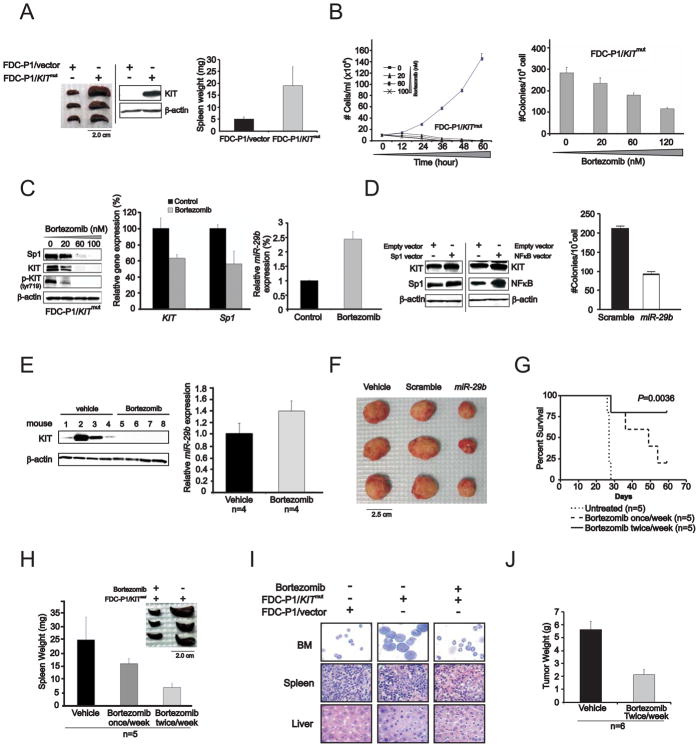
Figure 8. In vivo activity of bortezomib on KITmut-driven leukemia.
(A) Mice engrafted with FDC-P1/KITmut cells developed leukemia-like disease with enlarged spleens. Left: spleens from mice injected with FDC-P1/KITmut cells; Middle: immunoblotting indicated the presence of human KIT expression in the spleen from the mice engrafted with FDC-P1/KITmut cells, but not in FDC-P1/vector only cells. Right: graph of spleen weight (mean ± SD).
(B) Bortezomib inhibited proliferation (left panel) and colonogenic activity (right panel) in FDC-P1/KITmut cells (mean ± SEM).
(C) Bortezomib treatment decreased Sp1 and KIT protein (left panel) and RNA (middle panel) expression and increased miR-29b level (right panel) (mean ± SEM) in FDC-P1/KITmut cells. (D) Forced Sp1 and NFκB expression in FDC-P1/KITmut cells increased KIT level (left panel) and ectopic miR-29b expression inhibited the colonogenic activity in FDC-P1/KITmut cells (right panel) (mean ± SD). (E) KIT protein expression (left panel) was decreased and miR-29b transcription was increased (right panel) (mean ± SEM) in FDC-P1/KITmut cell engrafted mice 48 hours following in vivo treatment with bortezomib.
(F) Ectopic miR-29b expression significantly inhibits tumor growth in mice engrafted with FDC-P1/KITmut cells transfected with synthetic miR-29b.
(G) Bortezomib administered at the dose of 1mg/kg once a week or twice weekly increased survival duration in mice engrafted with FDC-P1/KITmut cells compared with untreated FDC-P1/KITmut cell engrafted controls.
(H) Spleens from FDC-P1/KITmut cell engrafted mice untreated versus bortezomib-treated (mean ± SD).
(I) May-Grumwald/Giemsa staining of BM cells and H&E staining of sections from spleen and liver of FDC-P1/KITmut cell engrafted mice untreated and bortezomib-treated. FDC-P1/empty vector cell engrafted mice were also used as control.
(J) Tumor growth was inhibited in mice engrafted with HMC-1 cell after the administration of bortezomib (mean ± SD).
Data are representatives of three independent experiments. (See also Figure S7)